Spinnor
Gold Member
- 2,227
- 419
Do parallel light rays diverge if ever so slightly upon exiting a spiral wave plate? See image below.
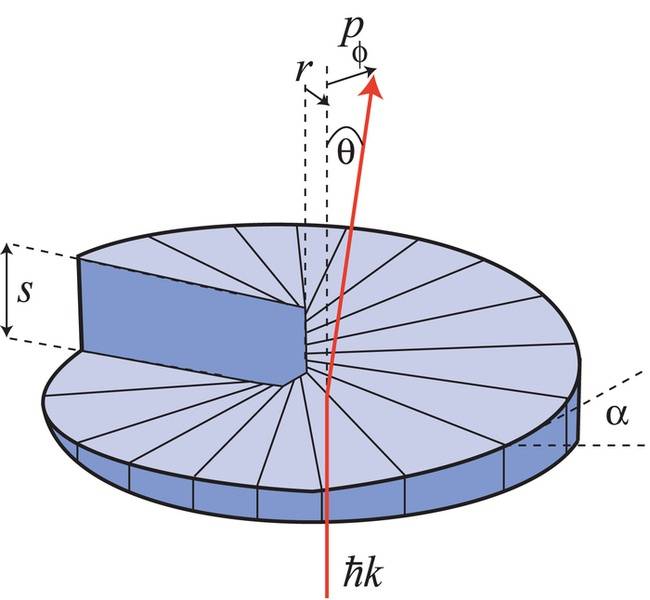
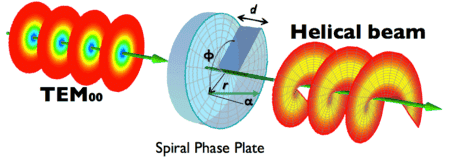
Images from,
https://www.google.com/search?q=spiral+phase+plate&safe=off&sa=X&es_sm=122&biw=1360&bih=649&tbm=isch&tbo=u&source=univ&ei=xEGDVcaKFYLV-AHZop_IAw&ved=0CC0QsAQ#imgrc=V_wYVTQHs9_JcM%3A;MIMazroQRD_VYM;http%3A%2F%2Fupload.wikimedia.org%2Fwikipedia%2Fcommons%2F1%2F1f%2FSpiral-phase-plate.png;http%3A%2F%2Fen.wikipedia.org%2Fwiki%2FAngular_momentum_of_light;1047;382
If there is divergence does that change the angular mementum of the light?
Thanks for any help!
Images from,
https://www.google.com/search?q=spiral+phase+plate&safe=off&sa=X&es_sm=122&biw=1360&bih=649&tbm=isch&tbo=u&source=univ&ei=xEGDVcaKFYLV-AHZop_IAw&ved=0CC0QsAQ#imgrc=V_wYVTQHs9_JcM%3A;MIMazroQRD_VYM;http%3A%2F%2Fupload.wikimedia.org%2Fwikipedia%2Fcommons%2F1%2F1f%2FSpiral-phase-plate.png;http%3A%2F%2Fen.wikipedia.org%2Fwiki%2FAngular_momentum_of_light;1047;382
If there is divergence does that change the angular mementum of the light?
Thanks for any help!