- #1
wkn0524
- 3
- 0
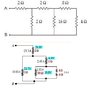
1. If the current in the 4.0 ohm resistor is 1.4A. What is the magnitude of the potential difference. Va-Vb?
2. V=IR, 1/Req=1/r1 +1/r2 ...
3. Va-Vb= 48V
I was stuck on beginning of the question. I knew how to start if the voltage is given but now asking me to find the potential difference and make me headache. I'm a beginner on the electrical course.
Thank.
2. V=IR, 1/Req=1/r1 +1/r2 ...
3. Va-Vb= 48V
I was stuck on beginning of the question. I knew how to start if the voltage is given but now asking me to find the potential difference and make me headache. I'm a beginner on the electrical course.
Thank.