- #1
closer
- 18
- 0
A 6.00 kg block is set into motion up an inclined plane with an initial speed of v0 = 8.50 m/s (Fig. P7.23). The block comes to rest after traveling 3.00 m along the plane, which is inclined at an angle of 30.0° to the horizontal.
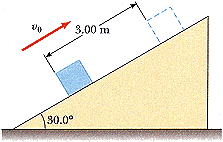
(a) Determine the friction force exerted on the block (assumed to be constant).
(b) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction?
Wfk + Wg = -.5mvi2
(fk)(x) + (m)(g)(h) = (-.5)(m)(vi2)
(fk)(3) + (6)(9.8)(3sin30) = (-.5)(6)(8.5^2)
fk = -101.65
Final answer is incorrect. Cannot move on to (b) without understanding (a). Any ideas?
(a) Determine the friction force exerted on the block (assumed to be constant).
(b) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction?
Wfk + Wg = -.5mvi2
(fk)(x) + (m)(g)(h) = (-.5)(m)(vi2)
(fk)(3) + (6)(9.8)(3sin30) = (-.5)(6)(8.5^2)
fk = -101.65
Final answer is incorrect. Cannot move on to (b) without understanding (a). Any ideas?
