better
- 1
- 0
TL;DR Summary: Independence of potential( inside a rectangular pipe running along z axis)from z coordinate
Consider the following diagram
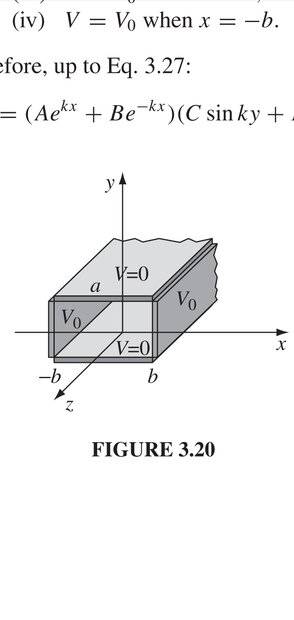
It is an infinite rectangular pipe running along z axis.I know that the potential inside the pipe is independent of z coordinate, but I cannot seem to convince myself of it.My guess is that it has to do something with uniqueness theorem.
Consider the following diagram
It is an infinite rectangular pipe running along z axis.I know that the potential inside the pipe is independent of z coordinate, but I cannot seem to convince myself of it.My guess is that it has to do something with uniqueness theorem.