- #1
thermodynam..
- 1
- 0
1. Sketch the phase space of a weight free falling along the z coordinate (no
motion in other directions). Sketch the trajectory of the free fall including
impact on the ground.
2. Calculate the density of states, entropy, and temperature (all as a function of
energy) for the following model: Consider a 1 dimensional lattice with 3 elds
(periodic boundary conditions). Every lattice site can have the states ; 0; +.
Interaction energies are only between nearest neighbors and are E() = +4
E(++) = +3 E(+) = E(+) = 2 everything else E = 0. Sketch the highest
and lowest energy states.
3. Dierences: CanonicalMicrocanonical ensemble
Assume you have given a density of states as a function of energy
(E). This can be used to calculate canonical and microcanonical data.
(a) Discretize Energy in units of E and write down the entropy microcanoni-
cally.
(b) Give the partition sum in the canonical and the microcanonical ensemble
(as a function of the relevant observables).
(c) Assume you measure an observable as a function of energy A(E). Write
down its average canonically and microcanonically.
2.
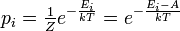
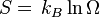
3. I don't know how to sketch in problem 1 and for problem 2, I think maybe there are mistakes in the problem, otherwise, the highest energy should be +∞ and the lowest is -∞. Problem 3 I totally have no idea of it, and I want to know the difference and relation between Ω(the number of microstates) and Ω'(the density of states).
motion in other directions). Sketch the trajectory of the free fall including
impact on the ground.
2. Calculate the density of states, entropy, and temperature (all as a function of
energy) for the following model: Consider a 1 dimensional lattice with 3 elds
(periodic boundary conditions). Every lattice site can have the states ; 0; +.
Interaction energies are only between nearest neighbors and are E() = +4
E(++) = +3 E(+) = E(+) = 2 everything else E = 0. Sketch the highest
and lowest energy states.
3. Dierences: CanonicalMicrocanonical ensemble
Assume you have given a density of states as a function of energy
(E). This can be used to calculate canonical and microcanonical data.
(a) Discretize Energy in units of E and write down the entropy microcanoni-
cally.
(b) Give the partition sum in the canonical and the microcanonical ensemble
(as a function of the relevant observables).
(c) Assume you measure an observable as a function of energy A(E). Write
down its average canonically and microcanonically.
2.
3. I don't know how to sketch in problem 1 and for problem 2, I think maybe there are mistakes in the problem, otherwise, the highest energy should be +∞ and the lowest is -∞. Problem 3 I totally have no idea of it, and I want to know the difference and relation between Ω(the number of microstates) and Ω'(the density of states).
Last edited by a moderator: