- #1
Nope
- 100
- 0
quick please..diagonalize matrix (row reduce)
http://www.math4all.in/public_html/linear algebra/chapter10.1.html
10.1.5 Examples: (ii)
this part:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
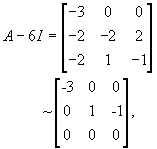
are both eigenvector for the eigenvalue λ = 3. Similarly, for λ = 6, since
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Does it matter if I reduce it to rref?
Homework Statement
http://www.math4all.in/public_html/linear algebra/chapter10.1.html
10.1.5 Examples: (ii)
this part:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
are both eigenvector for the eigenvalue λ = 3. Similarly, for λ = 6, since
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Does it matter if I reduce it to rref?