SUMMARY
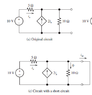
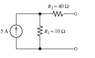
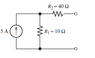
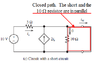
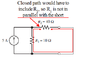
The discussion clarifies the concept of short circuits in electrical circuits, specifically addressing the confusion surrounding the resistance of components when short-circuited. When a circuit is short-circuited, the resistance of a resistor (R1) does not become zero if it is not directly in parallel with the short. The current divider principle is applied to find the short-circuit current (Isc) using the formula R1/(R1+r2), emphasizing the importance of understanding series and parallel connections in circuit analysis.
PREREQUISITES
- Fundamentals of electrical circuits
- Understanding of series and parallel resistor configurations
- Knowledge of the current divider principle
- Basic circuit analysis techniques
NEXT STEPS
- Study the fundamentals of series and parallel circuits
- Learn about the current divider principle in depth
- Explore Thevenin's theorem and its applications
- Practice circuit analysis problems involving short circuits
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and anyone looking to deepen their understanding of circuit analysis and short circuit behavior.