SUMMARY
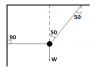
The discussion focuses on a physics problem involving a ball weighing 212 N suspended by cords at angles of 90 and 50 degrees. The key concept is the equilibrium of concurrent forces, where the sum of forces acting on the ball must equal zero. The tension in the horizontal and angled cords can be calculated using the principles of static equilibrium and the equation F=ma. The problem emphasizes the importance of understanding force diagrams and vector components in solving tension problems.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of static equilibrium principles
- Knowledge of vector components in physics
- Familiarity with Newton's laws of motion, specifically F=ma
- Ability to draw and interpret free-body diagrams
NEXT STEPS
- Study the concept of static equilibrium in detail
- Learn how to resolve forces into their vector components
- Practice solving tension problems using free-body diagrams
- Explore advanced topics in mechanics, such as dynamics of concurrent forces
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, particularly those focusing on mechanics and static equilibrium, as well as educators looking for examples of tension problems in real-world applications.