- #1
Hayool
- 14
- 0
The electric field
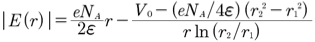 ...(1)
...(1)
by saying that
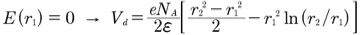 ...(2)I tried to integrate equation (1) from r2 to r1 but could not get equation(2).
...(2)I tried to integrate equation (1) from r2 to r1 but could not get equation(2).
Any suggesting.
Thanks
by saying that
Any suggesting.
Thanks
Thanks for your prompt respond.TSny said:Looks like you should be able to get (2) from (1) with just algebraic manipulation. Did you try letting ##E = 0## in (1) when ##r = r_1##and then solving for ## V##?
However, I get that (2) should have a positive sign for the last term.
Can you define the symbols ##V_d## and ##V_o## that occur in (1) and (2)?
The depletion voltage is the voltage at which the electric field in a semiconductor material is strong enough to deplete all the free carriers and create a depletion region, also known as the space charge region.
The depletion voltage can be calculated using the equation Vd = qNdL^2 / 2ε, where Vd is the depletion voltage, q is the elementary charge, Nd is the donor concentration, L is the width of the semiconductor material, and ε is the permittivity of the material.
The electric field in the depletion region is a constant value that is equal to the depletion voltage divided by the width of the depletion region. This value is typically in the range of 10^5 to 10^6 V/m.
The depletion voltage plays a crucial role in the operation of a semiconductor device. It controls the width of the depletion region, which in turn affects the device's capacitance, resistance, and conductivity. It also determines the threshold voltage for the device to turn on.
The depletion voltage can be affected by various factors, such as the doping concentration, temperature, and applied external voltage. Changes in these factors can alter the width of the depletion region and thus impact the depletion voltage. Additionally, the type of semiconductor material and its properties can also influence the depletion voltage.