Monsu
- 38
- 1
hi,
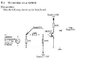
could anyone pls tell me why the storage time of a transistor changes as u change the position of one resistor?
During an experiment, when the resistor connected to the base voltage was reconnected to the ground i noticed that the storage time increased. pls someone explain to me why.
thanks!
(i'd appreciate multiple answers, so pls if smne has answered, pls feel free to drop your own answers too.)
Monsu
I'm not sure what you mean by "storage time," as this is not a parameter I've ever heard of. Can you please try describing your question in more standard terminology?
- Warren
the storage time is the time needed for minority carrier concentration in the vincinity of pn junction to be reduced to zero
could anyone pls tell me why the storage time of a transistor changes as u change the position of one resistor?
During an experiment, when the resistor connected to the base voltage was reconnected to the ground i noticed that the storage time increased. pls someone explain to me why.
thanks!
(i'd appreciate multiple answers, so pls if smne has answered, pls feel free to drop your own answers too.)
Monsu
I'm not sure what you mean by "storage time," as this is not a parameter I've ever heard of. Can you please try describing your question in more standard terminology?
- Warren
the storage time is the time needed for minority carrier concentration in the vincinity of pn junction to be reduced to zero
Last edited: