bryanso
- 28
- 7
- TL;DR
- Want to understand why the radiation term in Feynman's relativistic electric field equation (Eq. 28.3) is inversely proportional to distance
Feynman's Lectures, vol. 1 Ch. 28, Eq. 28.3 is
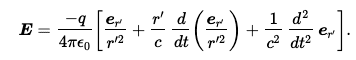
##r'## is the distance to the apparent position of the charge. Feynman wrote,
"Of the terms appearing in (28.3), the first one evidently goes inversely as the square of the distance, and the second is only a correction for delay, so it is easy to show that both of them vary inversely as the square of the distance. All of the effects we are interested in come from the third term, which is not very complicated, after all. What this term says is: look at the charge and note the direction of the unit vector (we can project the end of it onto the surface of a unit sphere). As the charge moves around, the unit vector wiggles, and the acceleration of that unit vector is what we are looking for. That is all. Thus

is a statement of the laws of radiation, because that is the only important term when we get far enough away that the fields are varying inversely as the distance."
I don't understand why this acceleration is inversely proportional to ##r'##?
Is that simply because the size of an object is inversely proportional to distance (perception) thus acceleration should be the same? Shouldn't ##\frac{1}{r}## appear somewhere?
(BTW this equation is extremely elegant but doesn't seem to be widely described in other texts.)
##r'## is the distance to the apparent position of the charge. Feynman wrote,
"Of the terms appearing in (28.3), the first one evidently goes inversely as the square of the distance, and the second is only a correction for delay, so it is easy to show that both of them vary inversely as the square of the distance. All of the effects we are interested in come from the third term, which is not very complicated, after all. What this term says is: look at the charge and note the direction of the unit vector (we can project the end of it onto the surface of a unit sphere). As the charge moves around, the unit vector wiggles, and the acceleration of that unit vector is what we are looking for. That is all. Thus
is a statement of the laws of radiation, because that is the only important term when we get far enough away that the fields are varying inversely as the distance."
I don't understand why this acceleration is inversely proportional to ##r'##?
Is that simply because the size of an object is inversely proportional to distance (perception) thus acceleration should be the same? Shouldn't ##\frac{1}{r}## appear somewhere?
(BTW this equation is extremely elegant but doesn't seem to be widely described in other texts.)