- #1
colorofeternity
- 2
- 0
- TL;DR Summary
- Is it possible to be able to use the Stefan Boltzmann law for a system which is being constantly heated and is in contact with a perfect vacuum (T = 0K).
Hi everyone,
I am currently trying to work something out in regards to non-equilibrium thermodynamics. If I have a block of metal in vacuum that is being heated by a laser with a constant power P, is it even possible to be able to describe the emission of radiation by the block via the Stefan Boltzmann law (ie E ~ T^4).
The reason why I ask this is that the Stefan-Boltzmann law can be derived from Planck's Radiation law which implicitly assumes that the system is in equilibrium with its surrounding. Clearly that is not occurring in this problem. Any suggestions for what should be used?
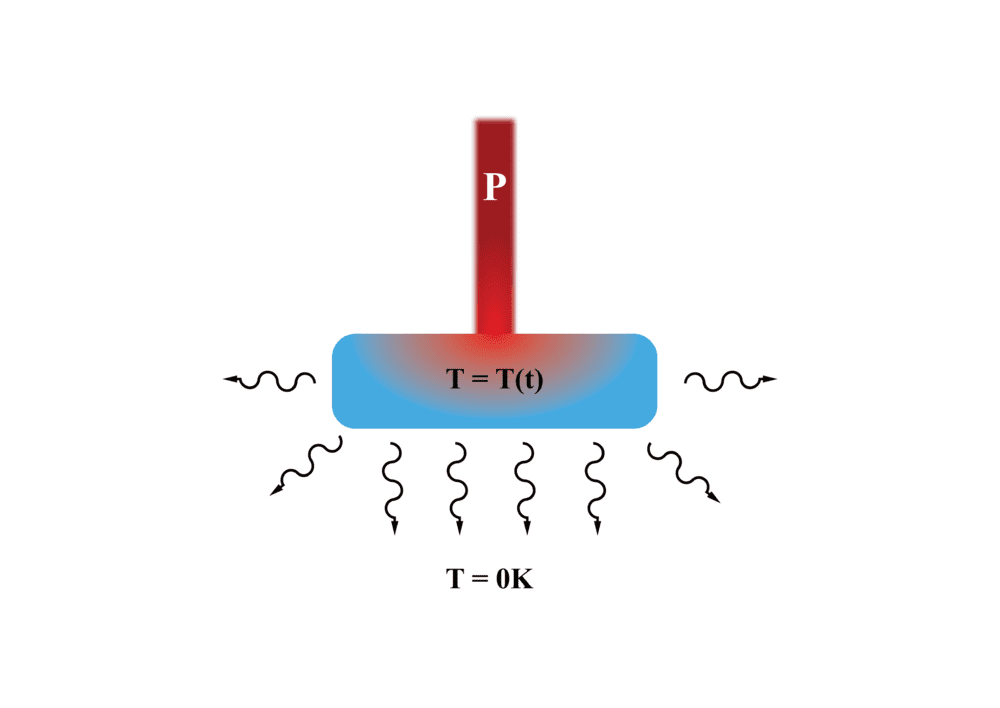
I am currently trying to work something out in regards to non-equilibrium thermodynamics. If I have a block of metal in vacuum that is being heated by a laser with a constant power P, is it even possible to be able to describe the emission of radiation by the block via the Stefan Boltzmann law (ie E ~ T^4).
The reason why I ask this is that the Stefan-Boltzmann law can be derived from Planck's Radiation law which implicitly assumes that the system is in equilibrium with its surrounding. Clearly that is not occurring in this problem. Any suggestions for what should be used?