- #1
Manganese
- 9
- 0
- TL;DR Summary
- Would connecting a battery in series with a voltaic cell accelerate the rate of the redox reaction of the cell?
Hello,
I wanted to know if connecting a battery in series with a voltaic cell would increase the rate of the redox reactions.
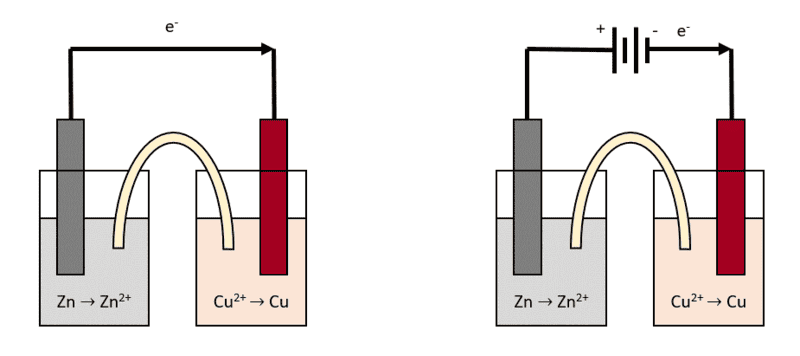
Let's take the simplest example of a voltaic cell constituted by a Zn/Zn2+ half-cell connected to a Cu/Cu2+ half-cell. When the circuit is closed, the Zn electrode will get corroded and will dissolve in Zn2+, while the Cu2+ ions in the other half-cell will get reduced to Cu.
What I wanted to know is, if I connect a battery in series with this voltaic cell (maintaining the same current direction), the potential difference should stack (if the Zn/Cu cell has a potential of 1.10 V, connecting a 3V battery in series should bring it to 4.10 V).
Will this potential increase somehow affect the rate of the redox reaction? Or the increase of the potential only affects the thermodynamics of the process (as in, it's just higher voltage) but the kinetics are unaffected? And also, would connecting a battery in series with this type of voltaic cell result in shorting the battery? I know they are getting discharged, but would this be happening at a fast rate or the voltaic cell acts as some sort of resistance?
I drew a sketch
I wanted to know if connecting a battery in series with a voltaic cell would increase the rate of the redox reactions.
Let's take the simplest example of a voltaic cell constituted by a Zn/Zn2+ half-cell connected to a Cu/Cu2+ half-cell. When the circuit is closed, the Zn electrode will get corroded and will dissolve in Zn2+, while the Cu2+ ions in the other half-cell will get reduced to Cu.
What I wanted to know is, if I connect a battery in series with this voltaic cell (maintaining the same current direction), the potential difference should stack (if the Zn/Cu cell has a potential of 1.10 V, connecting a 3V battery in series should bring it to 4.10 V).
Will this potential increase somehow affect the rate of the redox reaction? Or the increase of the potential only affects the thermodynamics of the process (as in, it's just higher voltage) but the kinetics are unaffected? And also, would connecting a battery in series with this type of voltaic cell result in shorting the battery? I know they are getting discharged, but would this be happening at a fast rate or the voltaic cell acts as some sort of resistance?
I drew a sketch
Last edited by a moderator: