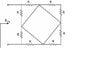
SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on calculating the equivalent resistance of resistors arranged in series and parallel configurations, specifically when all resistors have the same value, 'R'. Participants clarify that mesh and nodal analysis are unnecessary for this problem, emphasizing the importance of understanding the arrangement of resistors. The "diamond" configuration in the circuit is identified as having zero resistance, which is crucial for determining current flow in the circuit. This type of problem is common in introductory electronics courses and is designed to challenge students' understanding of series and parallel resistance concepts.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of series and parallel resistor configurations
- Familiarity with basic circuit theory
- Knowledge of Ohm's Law
- Ability to visualize circuit diagrams
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of series and parallel resistance calculations
- Learn about circuit simplification techniques
- Explore the concept of equivalent resistance in complex circuits
- Review practical applications of resistors in electronic circuits
USEFUL FOR
Students in introductory electronics courses, educators teaching circuit theory, and anyone seeking to improve their understanding of resistor configurations and equivalent resistance calculations.