You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What should be the particular solution?
- Thread starter tony_engin
- Start date
-
- Tags
- Particular solution
Physics news on Phys.org
Pyrrhus
Homework Helper
- 2,180
- 0
Yes it's ok.
dextercioby
Science Advisor
- 13,394
- 4,064
Or you can do it by the method of variation of constants.I've always thought of it as being elegant...
Daniel.
Daniel.
Pyrrhus
Homework Helper
- 2,180
- 0
Yes you should try
x^{2}e^{-2x}(Ax \cos 2x + Bx \sin 2x + C)
There are other methods for solving nonhomogenous constant coefficients ODEs such as Anulator Method by using the differential operator, and also Variation of parameters.
Here's a preview of the Anulator Method.
Imagine a ODE
y'' + 3y' + 2y = 4x^2
if we rewrite the above ODE with the differential operator D
(D^2 + 3D +2)y = 4x^2
Now if we use a differential operator D^3 we could eliminate 4x^{2}
D^3(D^2 + 3D +2)y = 4 D^3 x^2
D^3(D^2 + 3D +2)y = 0
Thus making a fifth grade auxiliary equation. There are more steps it was just a preview.
x^{2}e^{-2x}(Ax \cos 2x + Bx \sin 2x + C)
There are other methods for solving nonhomogenous constant coefficients ODEs such as Anulator Method by using the differential operator, and also Variation of parameters.
Here's a preview of the Anulator Method.
Imagine a ODE
y'' + 3y' + 2y = 4x^2
if we rewrite the above ODE with the differential operator D
(D^2 + 3D +2)y = 4x^2
Now if we use a differential operator D^3 we could eliminate 4x^{2}
D^3(D^2 + 3D +2)y = 4 D^3 x^2
D^3(D^2 + 3D +2)y = 0
Thus making a fifth grade auxiliary equation. There are more steps it was just a preview.
Last edited:
tony_engin
- 45
- 0
For the first differential equation that I firtsly raised, the answer of the particular solution should be something like "[1+xcosx] exp(-2x)" as given by the book. So I think the trial form should not be "[Asinx + Bcosx + C] exp(-2x)", right? So, what should be the correct form?
dextercioby
Science Advisor
- 13,394
- 4,064
I've already given you the hint to do it.It's up to you if u prefer other method,just as long as it leads to the result.The correct one.
Daniel.
Daniel.
tony_engin
- 45
- 0
um...you mean do it by variation of constants?
Since this is an exercise in trying the particular solution, I would like to know the form of the trial particular solution.
Since this is an exercise in trying the particular solution, I would like to know the form of the trial particular solution.
dextercioby
Science Advisor
- 13,394
- 4,064
One of the solution of the homogenous one contains that e^{-2x},so that should give a hint on how to pick the trial function.
Daniel.
Daniel.
tony_engin
- 45
- 0
I previously thought that I should try "[Asinx + Bcosx + C] exp(-2x)"
but the answer given by the book shows that this is wrong..
but the answer given by the book shows that this is wrong..
dextercioby
Science Advisor
- 13,394
- 4,064
Of course.You need an "x" to multiply the exponential,because the exponential is contained both in the solution of the hom.eq. and in the nonhomogeneity term.
Daniel.
Daniel.
tony_engin
- 45
- 0
So, it should be "[(Asinx + Bcosx)x + C] exp(-2x)" or "x[Asinx + Bcosx + C] exp(-2x)"?
dextercioby
Science Advisor
- 13,394
- 4,064
The first without the C,it's useless there.
Daniel.
Daniel.
Pyrrhus
Homework Helper
- 2,180
- 0
If you're still referring to your ODE.
y_{p_{1}} = Ce^{-2x}
y_{p_{2}} = xe^{-2x}(A \cos x + B \sin x)
y_{p} = Ce^{2x} + xe^{-2x}(A \cos x + B \sin x)
y_{p_{1}} = Ce^{-2x}
y_{p_{2}} = xe^{-2x}(A \cos x + B \sin x)
y_{p} = Ce^{2x} + xe^{-2x}(A \cos x + B \sin x)
saltydog
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 1,590
- 3
Tony, where are you with this? Getting it?
This is what I'd do (other than just plug it into Mathematica):
I tell you what, since the RHS is a particular solution to the homogeneous ODE:
(D+2)(D^2+4D+5)y=0\quad\text{(1)}\quad
you can apply this operator to both sides of the original equation to aniliate the RHS, that is:
If you have:
y^{''}+4y^{'}+5y=e^{-2x}(1+Cos(x))\quad\text{(2)}\quad
Applying the differential operator in (1) to both sides yields:
(D+2)(D^2+4D+5)(D^2+4D+5)y=0\quad\text{(3)}\quad
Right?
The solution of (3) will contain the solution of (2), just gets messy that's all.
So the solution of (3) is:
y(x)=c_1e^{-2x}+c_2e^{-2x}Cos(x)+c_3e^{-2x}Sin(x)+c_4xe^{-2x}Cos(x)+c_5xe^{-2x}Sin(x)
And thus a particular solution of (2) will be:
y_p(x)=Ae^{-2x}+Bxe^{-2x}Cos(x)+Cxe^{-2x}Sin(x)
Now what? How about a plot of the solution (just make up some initial conditions)?
This is what I'd do (other than just plug it into Mathematica):
I tell you what, since the RHS is a particular solution to the homogeneous ODE:
(D+2)(D^2+4D+5)y=0\quad\text{(1)}\quad
you can apply this operator to both sides of the original equation to aniliate the RHS, that is:
If you have:
y^{''}+4y^{'}+5y=e^{-2x}(1+Cos(x))\quad\text{(2)}\quad
Applying the differential operator in (1) to both sides yields:
(D+2)(D^2+4D+5)(D^2+4D+5)y=0\quad\text{(3)}\quad
Right?
The solution of (3) will contain the solution of (2), just gets messy that's all.
So the solution of (3) is:
y(x)=c_1e^{-2x}+c_2e^{-2x}Cos(x)+c_3e^{-2x}Sin(x)+c_4xe^{-2x}Cos(x)+c_5xe^{-2x}Sin(x)
And thus a particular solution of (2) will be:
y_p(x)=Ae^{-2x}+Bxe^{-2x}Cos(x)+Cxe^{-2x}Sin(x)
Now what? How about a plot of the solution (just make up some initial conditions)?
Last edited:
saltydog
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 1,590
- 3
Just some follow up:
Well, if you substitute y_p(x) into (2) above, it gets a little messy, do this and that, equate coefficients, some things cancel, and we're left with:
y_p(x)=e^{-2x}+\frac{1}{2}xe^{-2x}Sin(x)
So that the general solution is:
y(x)=c_1e^{-2x}Cos(x)+c_2e^{-2x}Sin(x)+e^{-2x}+\frac{1}{2}xe^{-2x}Sin(x)
Letting:
y(0)=1
y'(0)=1
we get:
y(x)=3e^{-2x}Sin(x)+e^{-2x}+\frac{1}{2}xe^{-2x}Sin(x)
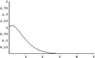
I've attached a plot of this solution. Tony, you can do all this right?
Well, if you substitute y_p(x) into (2) above, it gets a little messy, do this and that, equate coefficients, some things cancel, and we're left with:
y_p(x)=e^{-2x}+\frac{1}{2}xe^{-2x}Sin(x)
So that the general solution is:
y(x)=c_1e^{-2x}Cos(x)+c_2e^{-2x}Sin(x)+e^{-2x}+\frac{1}{2}xe^{-2x}Sin(x)
Letting:
y(0)=1
y'(0)=1
we get:
y(x)=3e^{-2x}Sin(x)+e^{-2x}+\frac{1}{2}xe^{-2x}Sin(x)
I've attached a plot of this solution. Tony, you can do all this right?
Attachments
Similar threads
- Replies
- 52
- Views
- 7K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 4K
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 17K
Hot Threads
-
I Understanding Legendre differential equation
- Started by chwala
- Replies: 2
- Differential Equations
-
I Visual Representation of Separation of Varables
- Started by sonnichs
- Replies: 4
- Differential Equations
-
I Why Lagrange’s method of solving Pp + Qq=R works?
- Started by PLAGUE
- Replies: 3
- Differential Equations
-
A Should the boundary condition have to satisfy dimensional consistency?
- Started by SaleemKU
- Replies: 6
- Differential Equations
-
A Show positivity and boundedness of a non-linear system
- Started by dgf
- Replies: 2
- Differential Equations
Recent Insights
-
Insights Why Entangled Photon-Polarization Qubits Violate Bell’s Inequality
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 7
- Quantum Physics
-
Insights Quantum Entanglement is a Kinematic Fact, not a Dynamical Effect
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 11
- Quantum Physics
-
Insights What Exactly is Dirac’s Delta Function? - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 5
- General Math
-
Insights Relativator (Circular Slide-Rule): Simulated with Desmos - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 1
- Special and General Relativity
-
Insights Fixing Things Which Can Go Wrong With Complex Numbers
- Started by PAllen
- Replies: 10
- General Math
-
Insights Fermat's Last Theorem
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 105
- General Math