Discussion Overview
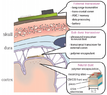
The discussion centers on the dimensions and characteristics of piezocrystals required to stimulate a typical nerve, exploring the relationship between piezoelectric properties and nerve depolarization. It includes technical considerations related to electrical stimulation, capacitor design, and the biological mechanisms of action potentials.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant inquires about the dimensions of a high-performing synthetic piezocrystal necessary for nerve stimulation and expresses interest in calculating the required volume.
- Another participant emphasizes the importance of defining the electrical parameters (current, voltage, time, charge) needed to stimulate a nerve before sizing the crystal.
- Steps for calculating the necessary capacitor to store charge and the need to account for energy losses in the circuit are outlined by one participant.
- There is a reiteration of the steps to connect a piezoelectric generator to a capacitor, highlighting the inefficiencies in energy harvesting.
- A biology major shares insights on the biological process of action potentials and questions the placement of electrodes for effective depolarization, indicating uncertainty about the flow of charge and the role of the capacitor.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express varying levels of understanding and approaches to the problem, with no consensus on the specific dimensions or configurations of the piezocrystal or the electrical setup required for nerve stimulation. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the optimal methods and parameters.
Contextual Notes
Participants note the complexity of the problem, including the need for iterative calculations and the dependence on specific electrical and biological parameters, which are not fully defined in the discussion.