bibo_dvd
- 37
- 0
hello guys
while studing the diode limitters
i found two examples i solved the first one but i couldn't with the second
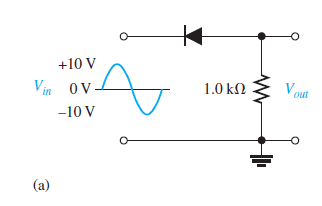
1 -
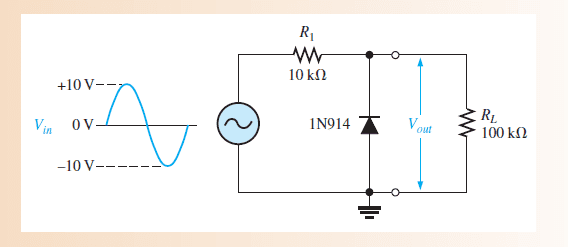
2-
in the first i know that the diode while be forward biased in the negative half of the signal
so the negative half will be limitted to -0.7 v
and the V peak output will be = [(RL/(RL+R1)]*Vinput = 9.09v
but i don't know what will be the difference between the first and the second problem !
so please help me guys ...Thanks :)
while studing the diode limitters
i found two examples i solved the first one but i couldn't with the second
1 -
2-
in the first i know that the diode while be forward biased in the negative half of the signal
so the negative half will be limitted to -0.7 v
and the V peak output will be = [(RL/(RL+R1)]*Vinput = 9.09v
but i don't know what will be the difference between the first and the second problem !
so please help me guys ...Thanks :)