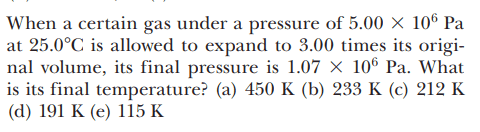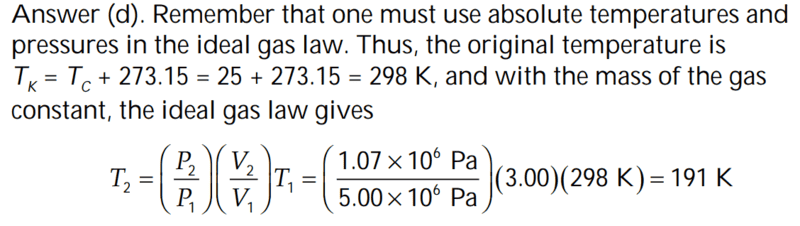Homework Help Overview
The discussion revolves around the necessity of using absolute temperature in the Ideal Gas Law, specifically questioning why Celsius cannot be used as a valid temperature scale. Participants explore the implications of temperature scales on calculations involving gas laws.
Discussion Character
- Conceptual clarification, Assumption checking, Mixed
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Some participants attempt to explain the origins of temperature scales and their implications for the Ideal Gas Law. Others question the consequences of using Celsius, particularly at zero degrees, and how it could lead to erroneous interpretations of physical situations. There are discussions about the nature of absolute zero and its relevance to the gas law.
Discussion Status
The discussion is ongoing, with various perspectives being shared. Some participants provide insights into the historical context of temperature scales, while others emphasize the importance of absolute zero in avoiding inconsistencies in calculations. There is no explicit consensus, but multiple interpretations are being explored.
Contextual Notes
Participants note the potential confusion arising from using temperature scales that do not start at absolute zero, as well as the implications of using different units in scientific formulas. The conversation reflects a mix of theoretical and practical considerations regarding temperature measurement in the context of gas laws.