- #1
zenterix
- 480
- 70
- Homework Statement
- In the table below, a number in the top row represents the pressure of a gas in the bulb of a constant-volume gas thermometer (corrected for dead space, thermal expansion of bulb, etc) when the bulb is immersed in a water triple-point cell. The bottom row represents the corresponding readings of pressure when the bulb is surrounded by a material at a constant unknown temperature.
Calculate the ideal-gas temperature of this material to five significant figures.
- Relevant Equations
- Please see table and calculations in what follows.
Here is the table
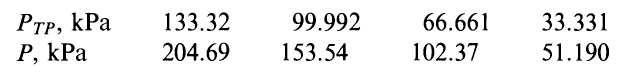 As far as I can tell what we have here are four constant-volume thermometers (each column represents a thermometer). These thermometers work by having a certain constant volume of some specific gas in a bulb. We immerse the bulb in whatever temperature we would like to measure, and measure the pressure required to keep the volume constant.
As far as I can tell what we have here are four constant-volume thermometers (each column represents a thermometer). These thermometers work by having a certain constant volume of some specific gas in a bulb. We immerse the bulb in whatever temperature we would like to measure, and measure the pressure required to keep the volume constant.
Then we use the equation ##\theta(P)=273.16\frac{P}{P_{TP}}## where ##P_{TP}## is the pressure of the thermometer in question when immersed in the water triple-point cell.
For the four thermometers in this problem we have

Notice that for each successive thermometer, the triple point pressure is lower. This happens because the amount of constant volume is successively larger for each thermometer.
If we keep reducing the constant volume and measuring the pressure of the unknown material, we will reach some limiting value
$$\lim\limits_{P_{TP}\to 0} 237.16\cdot\frac{P}{P_{TP}}$$
Now, I don't see how to calculate this limit other than to extrapolate from the observed values.
If we plot the constant volume of each thermometer vs the empirical temperature using that thermometer then we get the following
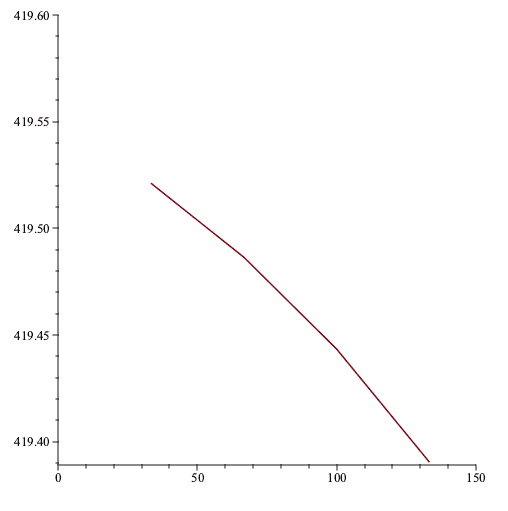
The ideal-gas temperature would be wherever the plot intercepts the vertical axis, let's call it 419.55K.
Is this correct?
When I look at the answer at the end of the book I am reading, it says the answer is 1.5356K. This seems to be related to the ratio of pressures only, not the ratio times the triple point temperature in kelvin. That is,

Why is the book calling this the ideal-gas temperature? Or is it an error?
The book is "Heat and Thermodynamics", Seventh Edition, by Zemansky and Dittman, and the problem is 1.1 (Chapter 1, problem 1).
Then we use the equation ##\theta(P)=273.16\frac{P}{P_{TP}}## where ##P_{TP}## is the pressure of the thermometer in question when immersed in the water triple-point cell.
For the four thermometers in this problem we have
Notice that for each successive thermometer, the triple point pressure is lower. This happens because the amount of constant volume is successively larger for each thermometer.
If we keep reducing the constant volume and measuring the pressure of the unknown material, we will reach some limiting value
$$\lim\limits_{P_{TP}\to 0} 237.16\cdot\frac{P}{P_{TP}}$$
Now, I don't see how to calculate this limit other than to extrapolate from the observed values.
If we plot the constant volume of each thermometer vs the empirical temperature using that thermometer then we get the following
The ideal-gas temperature would be wherever the plot intercepts the vertical axis, let's call it 419.55K.
Is this correct?
When I look at the answer at the end of the book I am reading, it says the answer is 1.5356K. This seems to be related to the ratio of pressures only, not the ratio times the triple point temperature in kelvin. That is,
Why is the book calling this the ideal-gas temperature? Or is it an error?
The book is "Heat and Thermodynamics", Seventh Edition, by Zemansky and Dittman, and the problem is 1.1 (Chapter 1, problem 1).