You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Fundamental: Definition and 946 Discussions
Given a topological space and a group acting on it, the images of a single point under the group action form an orbit of the action. A fundamental domain or fundamental region is a subset of the space which contains exactly one point from each of these orbits. It serves as a geometric realization for the abstract set of representatives of the orbits.
There are many ways to choose a fundamental domain. Typically, a fundamental domain is required to be a connected subset with some restrictions on its boundary, for example, smooth or polyhedral. The images of a chosen fundamental domain under the group action then tile the space. One general construction of fundamental domains uses Voronoi cells.
View More On Wikipedia.org
There are many ways to choose a fundamental domain. Typically, a fundamental domain is required to be a connected subset with some restrictions on its boundary, for example, smooth or polyhedral. The images of a chosen fundamental domain under the group action then tile the space. One general construction of fundamental domains uses Voronoi cells.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-

Technological mastery of fundamental forces
This may be an overly-broad question, but is there any reason to think we will ever have the technical mastery over gravity, the strong force, and the weak force, that we have over electromagnetism? Example: turn on a switch, gravity; turn off a switch, no gravity.- Khatti
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Sci-Fi Writing and World Building
-

I Excited hadrons v. fundamental particles
Mesons and baryons have both a ground state and excited states involving the same valence quarks but a higher mass (which can in principle be calculated from QCD). Fundamental fermions and bosons, however, do not appear to display this behavior. They have a ground state, and while there are...- ohwilleke
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-

B Fundamental Constants: How Do We Know They're Constant?
How do we know that constants in nature like the Gravitational constant or plank's constants are actually "constant" and don't actually change over time? What sorts of experiments have been done which verify these things?- PumpkinCougar95
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Constants Fundamental
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-

Modular Forms, Fundamental Domain Question
Homework Statement My question is below it makes more sense there, after I have gave my interpretation of the definition of the fundamental domain to confirm my understanding Homework Equations The fundamental domain is defined as: 1) Every point in H is equivalent to a point in F. 2)...- binbagsss
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Domain Forms Fundamental
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-

B The values of the fundamental constants
The reason for initiating this thread is to have read another, initiated by Serra Nova here in the forum, accessible at the following address. https://www.physicsforums.com/threads/fundamental-physical-constants.938267/ The starting note of this thread refers to knowing if those terms called...- slow
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Constants Fundamental
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-

Application of the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (cosmological red-shift)
Homework Statement [/B] I am stuck on the section of my lecture notes attached, where it says that equation 4.20 follows from 4.18 via an application of the fundamental theorem of calculus Homework Equations FoC: if ## f## is cts on ##[a,b]## then the function ...- binbagsss
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-

B Is the time dimension more fundamental?
If we do the thougt experiment to delete one of the three spacedimentions we end up with a flat-land universe, which is fully possible to imagine (while probably not existing) But if we delete the time dimesion it becomes inpossible to imagin. Whithout time there is no existence. Could that mean...- thermia
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Dimension Fundamental Time
- Replies: 34
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-

MHB Fundamental theorem of calculus and more....
So as always I come here to make sure my maths homework is right and ask few questions to make sure I understand the topic. Here is my homework: Q.1 I'm fairly certain that this is correct, however, please check if I didn't do any stupid mistakes. Q.2 Same as above. Q.3 Now here is where the... -

I Fundamental physical constants
Why are the fundamental physical constants called "constants" when they change over time? I've read that the constants were adjusted in 1986. How can there even be something that is constant, when we can't even see the entire universe?- Serra Nova
- Thread
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
W
Vector Integration: Fundamental theorem use
Homework Statement Could someone illustrate why $$\int_{V} \nabla \cdot (f\vec{A}) \ dv = \int_{V} f( \nabla \cdot \vec{A} ) \ dv + \int_{V} \vec{A} \cdot (\nabla f ) \ dv = \oint f\vec{A} \cdot \ d\vec{a}$$ ? Homework EquationsThe Attempt at a Solution I understand that the integrand can...- WWCY
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-

A Fundamental Theorem of Quantum Measurements
The Fundamental Theorem of Quantum Measurements (see page 25 of these PDF notes) is given as follows: Every set of operators ##\{A_n \}_n## where ##n=1,...,N## that satisfies ##\sum_{n}A_{n}A^{\dagger}_{n} = I##, describes a possible measurement on a quantum system, where the measurement has...- Danny Boy
- Thread
- Replies: 77
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

Insights The Fundamental Difference in Interpretations of Quantum Mechanics - Comments
Greg Bernhardt submitted a new PF Insights post The Fundamental Difference in Interpretations of Quantum Mechanics Continue reading the Original PF Insights Post.- PeterDonis
- Thread
- Replies: 190
- Forum: Quantum Interpretations and Foundations
-
B
B What is source of fundamental particle charge?
Hello, Analogous to mass of fundamental (not composite) particles coming from interaction of those particles with the Higg's Field, does charge of fundamental particles come from interaction of those particles with some known/hypothesized fundamental field? Thank you!- Berbit
- Thread
- Replies: 18
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
K
Measure with a zero-energy fundamental state
Homework Statement Given the following Hamiltonian: And the observable: Calculate the probability of measuring any of the possible values of A in the fundamental state. The attempt at a solution I have calculated the eigenvectors and eigenvalues of the Hamiltonian, being the eigenvalues...- Keru
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Fundamental Measure State
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
D
Fundamental noise limit for an ideal photodetector
Homework Statement As the title says, I'm trying to calculate the fundamental noise limit for an ideal photodetector, by specifically looking at the rate of incidence of annihilation of photons (and subsequent excitation of conducting electrons) on the detection surface. Since I'm looking for...- Dustgil
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-

What are the dominant forces in different situations?
I volunteered to help tutor students in a nearby high school in math and science. I got two seniors from an AP Physics class. I'm doing OK with most of the problems, but it's been almost 50 years since my last physics class, so I'm more than a little rusty in some details. I'm hoping I can get...- Wes Turner
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
J
A Fundamental sequences for the Veblen hierarchy of ordinals
I will first summarize the construction of ordinal numbers and introduce the definition of the binary Veblen function and of the notion of fundamental sequence. Ordinal numbers start with natural numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, ... which are followed by ## \omega ## which represents the "simple" infinity...- jacquesb
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Set Theory, Logic, Probability, Statistics
-
D
Fundamental Frequency Question
Homework Statement A stretched wire vibrates in its first normal mode at a frequency of 369Hz. What would be the fundamental frequency if the wire were one third as long, its diameter were tripled, and its tension were increased two-fold? Homework Equations f = 1/2L * squareroot(Ft/u) The...- dantechiesa
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

A Fundamental group of a sphere with 6 points removed
This space is homotopy equivalent to the complement of the three coordinate axes in ##R^3##. This is in the chapter about the Seifert-Van Kampen Theorem, so I'm expecting to invoke that theorem. The thing is, how should we choose our open sets such that the intersection is path connected and...- PsychonautQQ
- Thread
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Topology and Analysis
-
S
B Electromagnetic fields of fundamental particles -- help please
Hi, we know that the particles have intrinsic properties for them electric field and magnetic moment, but for what I mean particles, I mean quarks, the fundamental blocks of (protons, neutrons and mesons) with everything that nobody explained as electric and The magnetic field of a particle and...- sirios
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

A Fundamental group of n connect tori with one point removed
Well, for starters, ##\pi(T)##, the fundamental group of the torus, is ##\pi(S^1)x\pi(S^1)=## which is in turn isomorphic to the direct product of two infinite cyclic groups. Before I tackle the case of n connect tori with one point removed, I'm trying to just understand a torus with a point...- PsychonautQQ
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Topology and Analysis
-

A Fundamental group of Project Plane with 2 points missing
edit: fixed typo's andrewkirk pointed out, oops I can cover the projective plane with 2 open sets U,V where each of these neighborhood contains the point that is missing, and the intersection of these two neighborhoods will be simply connected. I was then hoping to invoke the Seifert-Van-Kampen...- PsychonautQQ
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Topology and Analysis
-

Fundamental Proofs in General Physics?
Hello, I'm a freshman and I'm struggling with some questions. I'm trying to relate all I'm learning from my Physics classes to the real world (that is the mathematical connection and its expanations with the real world). I have some especifics questions but also a general answer I think could be...- CollinsArg
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: STEM Academic Advising
-
A
Frequencies of fundamental standing waves
Homework Statement Homework Equations Harmonics equations The Attempt at a Solution So, I got (A), which is the answer key is correct, but I'm not sure whether my reasoning is right or not. Would this be considered a closed-end air column question? Anyways, according to the length-wavelength...- ardour
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

MHB Another Question On B&S, Theorem 7.3.5 - Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus ...
I am reading "Introduction to Real Analysis" (Fourth Edition) by Robert G Bartle and Donald R Sherbert ... I am focused on Chapter 7: The Riemann Integral ... I need help in fully understanding yet another aspect of the proof of Theorem 7.3.5 ...Theorem 7.3.5 and its proof ... ... read as...- Math Amateur
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Topology and Analysis
-

MHB Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus (Second Form) - B&S Theorem 7.3.5 .... ....
I am reading "Introduction to Real Analysis" (Fourth Edition) by Robert G Bartle and Donald R Sherbert ... I am focused on Chapter 7: The Riemann Integral ... I need help in fully understanding an aspect of the proof of Theorem 7.3.5 ...Theorem 7.3.5 and its proof ... ... read as follows: In...- Math Amateur
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Topology and Analysis
-

I Homotopy Class vs Fundamental Group.
They seem the same to me. So I can have many paths between a and b that are continuously deformable into each other while keeping the endpoints fixed. We say these function form a equivalence class [f]. This should be regardless if the endpoints are the same or not. The fundamental group seems...- FallenApple
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Topology and Analysis
-
H
Finding the equations of state via the fundamental relation
Homework Statement Homework Equations $$\frac{\partial S}{\partial u}\Bigr|_{v} = \frac{1}{T}$$ $$\frac{\partial S}{\partial v}\Bigr|_{u} = \frac{-P}{T}$$[/B] The Attempt at a Solution a.) $$\frac{S}{R} = \frac{UV}{N} - \frac{N^3}{UV}$$ $$\frac{S}{R} = \frac{UV}{N} - \frac{N}{uv}$$ $$...- hijasonno
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Advanced Physics Homework Help
-
A
B No new fundamental particles at CERN until today
I remember reading in some book, that the most important experiments are those that produce negative results: the Michelson-Morley experiment for example. The standard model is complete after the Higgs boson. I believe that if no new particle appears in CERN, it would be one of the greatest...- alejandromeira
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Beyond the Standard Models
-

Fundamental Group Coset to preimage bijection
Homework Statement Let p: E-->B be a covering map, let p(e_0)=b_0 and let E be path connected. Show that there is a bijection between the collection of right cosets of p*F(E,e_0) in F(B,b_0) (where p* is the homomorphism of fundamental groups induced by p and F(E,e_0),F(B,b_0) are the...- PsychonautQQ
- Thread
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Calculus and Beyond Homework Help
-
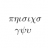
Fundamental thermodynamics relation
I was looking at the fundamental equation ##dU = Tds - Pdv + \sum_i \ \mu_i \ dN_i## and I was thinking of how many different ways one has for deriving it. I know I have to look through a book on Thermodynamics. I actually have done that some time ago and I will do that again. But the following...- davidge
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-

I Fundamental laws time reversal
It is often told that fundamental laws are insensitive to +t/-t change. Let's try this one: a little mass m1 object is accelerating towards a big object M2, in -x direction in space and +t in time, due to gravity or following space-time free fall line (along a geodetic). Now, revert the video...- Alfredo Tifi
- Thread
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
C
I Fundamental elements transformation
I wonder if it is possible to express a simple principle into a mathematical form. The simple principle says if at time t0 an isolated system is composed of some elements with some properties then at t1 it is composed of other elements with different properties, then in principle it is possible...- calinvass
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: General Math
-

Fundamental problem regarding mole concept
Background: Amount of substance is a fundamental physical quantity which has mole (mol) as it's SI unit. Therefore all expressions for amount of substance should have the unit mole on simplification. Therefore, if A = Amount of substance (normally in moles), m = Mass of the substance in a...- donaldparida
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Concept Fundamental Mole
- Replies: 6
- Forum: Chemistry
-
Proof of fundamental thermodynamics equation for open systems
Hi ! I'm having a bit of trouble understanding something. Let 'u' be internal energy, 'h' enthalpy, 'e' work and 'q' heat. ('r' are dissipations and 'S' entropy) From a book , i read that de+dr=PdV= -du + TdS This seems to stand for closed cycle. Yet, my teacher uses the formula de+dr=vdP=...- PHstud
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Thermodynamics
-

I Question about the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
Hi All, According to the fundamental theorem of algebra: "every non-zero, single-variable, degree n polynomial with complex coefficients has, counted with multiplicity, exactly n complex roots". My question is: what about polynomials with degree say 2.3 or 3.02, as in the polynomial: ## p(x) =...- DaTario
- Thread
- Replies: 14
- Forum: General Math
-

I Corollaries of the fundamental integral theorems
Can anyone please tell me significance of these corollaries of fundamental integral theorems? I can prove these corollaries but I don't understand why do we need to learn it? Do these corollaries have some physical significance? (a)$$\iiint_V(\nabla T)d^3 x=\oint_S T d\vec a$$ here S is the...- Pushoam
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Fundamental Integral
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
I The Fundamental Nature of Angular Momentum in Quantum Mechanics
My textbook "The physics of quantum mechanics" by James Binney and David Skinner, describes the pseudo-vector operators \vec{J}, \vec{L} & \vec{S} as generators of various transformations of the system. \vec{J} is the generator of rotations of the system as a whole, \vec{L} is the generator of...- Jezza
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Fundamental
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
S
I Constructing a 2nd order homogenous DE given fundamental solution
Homework Statement Given a set of fundamental solutions {ex*sinx*cosx, ex*cos(2x)} Homework Equations y''+p(x)y'+q(x)=0 det W(y1,y2) =Ce-∫p(x)dx The Attempt at a Solution I took the determinant of the matrix to get e2x[cos(2x)cosxsinx-2sin(2x)sinxcosx-cos(2x)sinxcosx-...- sagamore4110
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Differential Equations
-

A Valence formula- fundamental domain- why truncation height?
In the proof of the valence formula you integrate ##f'(t)/f(t)## around the boundary of the fundamental domain, with some modifications such as : - omitting the points ##i, \omega ## - since equivalence is allowed on the boundary, modifying as needed to ensure such points that are equivalent...- binbagsss
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Domain Formula Fundamental Height
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Linear and Abstract Algebra
-

I Theoretical Models for Sizes of Fundamental Particles
I am aware that according to the Standard Model of Particle Physics, fundamental particles such as electrons and quarks are treated as point-like particles. However, if fundamental particles are indeed 0-dimentional points with no spatial extent, it creates problems (i.e. fundamental particles...- Nathan Warford
- Thread
- Replies: 23
- Forum: High Energy, Nuclear, Particle Physics
-
L
I Dimensionless and dimensioned fundamental constants
There are 25 or so dimensionless constants in the standard models, such as the masses of the fundamental particles (that can be divided by Planck mass or some other mass to become dimensionless). And there are the three dimensionful constants c, h, G (speed of light, Planck's constant, Newton...- Lapidus
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Constants Fundamental
- Replies: 25
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-

B The fundamental units in Physics
I have been in my physics crash course for my entrance exam. I was looking at the chapter "Units and Measurement". I got a doubt in this chapter and I didn't get it cleared by my teacher. So I am posting this in this forum. We have 7 fundamental quantities and other quantities are derived...- Vengo
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-

I Why is it that the fundamental harmonic is louder than rest?
Why is it that the fundamental harmonic is louder than rest? If energy is the same as frequency surely the greater the harmonic the louder it is. Also what does amplitude represent in waves?- Theudius
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Fundamental Harmonic Rest
- Replies: 13
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
M
B Thermal and Non thermal light emission
I am now working on Thermal and Non-thermal light emission of materials, particular concerning the Planck law and Generalize Planck Law. I really want to understand the fundamental concept of this. So could you please suggest me some material, book on this subject? Thank you so much in advance,- Mengkoing
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Atomic and Condensed Matter
-
J
I If an electron isn't fundamental, what fields are it made of
http://www.nature.com/news/not-quite-so-elementary-my-dear-electron-1.10471 It was found out that electrons are made of quasi particles. But kind of fields are the quasiparticles made of?- joegibs
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Electron Fields Fundamental
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
R
Finding wavelength and fundamental frequency with string
The length of a string is 1328 cm. It is held fixed at each end. The string vibrates in eight sections; i.e., the string has eight antinodes, and the string vibrates at 97 Hz. Find the wavelength and fundamental frequency. I have no clue, anything helps! Thank you!- rachb75
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Electromagnetism
-

I Summary of the fundamental equations/laws
Hey, all! So, a friend of mine recently bought a shirt with a bunch of random, nonsensical formulas on them and it kind of seemed odd to me. So I had an idea for a T-shirt design with proper formulas... The basic, fundamental equations and laws of physics as we know them now. So far I have...- JoePhysics
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Fundamental
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
O
A Is the electron a fundamental particle?
According to this article an electron can be split into 3 quasiparticles: ‘holon’ carrying the electron’s charge ‘spinon’ carrying its spin ‘orbiton’ carrying its orbital location The article links to an experiment that was made in 2012, where physicists were able detect the spinion and the...- Ostrados
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-

I What mediates the exchange force?
In many-body theory for electronic structure, fermions experience a force resulting from Pauli Exclusion. So by extension, would quarks and other subatomic fermions experience this force? If so, what is the "high energy" physics side of the story to forces arising from exchange rules? Is it a...- Ben Wilson
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Exchange Force Fundamental Quarks
- Replies: 23
- Forum: Quantum Physics