You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
What is Light: Definition and 1000 Discussions
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation within the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). This wavelength means a frequency range of roughly 430–750 terahertz (THz).
The primary properties of visible light are intensity, propagation-direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum and polarization. Its speed in a vacuum, 299 792 458 metres a second (m/s), is one of the fundamental constants of nature, as with all types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), light is found in experimental conditions to always move at this speed in a vacuum.In physics, the term 'light' sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. Like all types of electromagnetic radiation, visible light propagates as waves. However, the energy imparted by the waves is absorbed at single locations the way particles are absorbed. The absorbed energy of the electromagnetic waves is called a photon and represents the quanta of light. When a wave of light is transformed and absorbed as a photon, the energy of the wave instantly collapses to a single location and this location is where the photon "arrives". This is what is called the wave function collapse. This dual wave-like and particle-like nature of light is known as the wave–particle duality. The study of light, known as optics, is an important research area in modern physics.
The main source of light on Earth is the Sun. Historically, another important source of light for humans has been fire, from ancient campfires to modern kerosene lamps. With the development of electric lights and power systems, electric lighting has effectively replaced firelight.
View More On Wikipedia.org
The primary properties of visible light are intensity, propagation-direction, frequency or wavelength spectrum and polarization. Its speed in a vacuum, 299 792 458 metres a second (m/s), is one of the fundamental constants of nature, as with all types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), light is found in experimental conditions to always move at this speed in a vacuum.In physics, the term 'light' sometimes refers to electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength, whether visible or not. In this sense, gamma rays, X-rays, microwaves and radio waves are also light. Like all types of electromagnetic radiation, visible light propagates as waves. However, the energy imparted by the waves is absorbed at single locations the way particles are absorbed. The absorbed energy of the electromagnetic waves is called a photon and represents the quanta of light. When a wave of light is transformed and absorbed as a photon, the energy of the wave instantly collapses to a single location and this location is where the photon "arrives". This is what is called the wave function collapse. This dual wave-like and particle-like nature of light is known as the wave–particle duality. The study of light, known as optics, is an important research area in modern physics.
The main source of light on Earth is the Sun. Historically, another important source of light for humans has been fire, from ancient campfires to modern kerosene lamps. With the development of electric lights and power systems, electric lighting has effectively replaced firelight.
View More On Wikipedia.org
-
G
B Does Light Energy contain Heat Energy in a large scale?
Can I understand that light energy contains heat energy? or Do I have to separate between two concepts? because light energy from the sun makes heat energy after absorption of molecular?- ggandy
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Energy Heat Heat energy Light Scale
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-

I What does "upright" mean in geometric optics?
if someone want to explain to me what is an upright image ? , and what are the other adjectives to define an image in geometric optics and their meaning , Thanks .- samy4408
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-

B Can You Become a Black Hole from Approaching Light Speed?
If you're in a relativistic starship, approaching the speed of light, then if you get too close to it, do you end up becoming a black hole? Relativistic length decreases as you get closer to light speed. Relativistic mass increases as you do the same. Will your relativistic mass and relativistic...- bbbl67
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black hole Hole Light Light speed Speed
- Replies: 25
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
B
Question on the Newtonian displacement of light
Hi everyone! Hope your day is going well. I’m an ex-physics student who recently wanted to go back to studying the subject (as a hobby, mostly). So I picked up Zee’s GR book since GR is the thing I’m the most interested in. I expected to hit a wall on some basic things since I’m rusty, and did...- brpetrucci
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
B Exploring Light with a DIY Spectroscope
Hello, I built myself a spectroscope with a CD (where I removed the coating), similar to this one: With this I now want to look at light sources. However, some interesting lamps are a bit too bright to comfortably look directly into (through the spectroscope). Does anyone have an idea how to...- DDesulgon
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Brightness Diy Light
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Optics
-

I with this Circular Aperature Diffraction Problem please
I know that in order for the two lights to be distinguishable from one another they have to be separated by an angle of at least theta = 1.22(wavelength)/(width of aperture). I tried drawing the given picture below and then using trig to find L in terms of d/2 and theta/2. However, this ended up...- AManFromSpace
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
D
B Proposed Experiment - Speed of Light
One of the reasons to suggest that light might be bent by gravity is the assumption that light is behaving as the other objects that bend their trajectories by gravity. On a similar ground, we could suggest that as the objects are experiencing Gravity Assist, then the light could be also...- DanAil
- Thread
- Replies: 30
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
S
B Light Speed in Vacuum: Does It Reach Cosmic Limit?
As we all know, light itself is the fastest thing in the universe, and the cosmic speed limit, basically. That said, it is said to go at 299,792,458 meters per second in a vacuum. That is pretty fast. However, I have a question I want to ask... Does light really go that fast in a vacuum? I ask...- Sundown444
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B For object 3.26 million light-years away, light redshifted by 70 km/s
Source: https://bigthink.com/starts-with-a-bang/fast-space-expanding/ I need help with the part in red. What does it mean when it says light is redshifted by 70 km/s? When the redshift occurs the wavelength increases which is measured in meters or kilometers. I don't understand the "per second"...- PainterGuy
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Light
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Cosmology
-
G
B Constant Speed of Light: Low Speed Explained
I understand the relativistic effects at high speeds, what accounts for the constant speed of light at low speeds? Example... If I travel towards a beam of light at 25 MPH, I will still measure the light as traveling towards me at the speed of light and not the speed of light plus 25 MPH.- grounded
- Thread
- Replies: 18
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
B
Orientation of Major Axis for polarized light
Case 1 worked out great, I found it to be linearly polarized light at an angle ##\alpha = \frac{\pi}{4}##, but Case 2 is giving me trouble. As best I can tell, ##\alpha## is undefined in case 2. How do I solve case 2?- Blanchdog
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
T
I Permittivity/Permeability, the speed of light, and the meter
Good evening all, I had a question on how the standard for the meter is defined. A simple Google search tells us that since 1983, the meter has been internationally defined as the length of the path traveled by light in vacuum during a time interval of 1 / 299, 792, 458 of a second. Many other...- TRB8985
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Light Meter Speed Speed of light
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
K
B Experience Travel on a Photon: Hitch-Hiker's Guide to the Universe
We know that as speed increases, time slows, and at the speed of light time apparently ceases. Imagine a hypothetical hitch-hiker sitting on a photon and speeding through the universe at -- well, the speed of light. If time has stopped for him (her?), what is his experience of his journey? Are...- Karl24
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
A
B Light and the black matter (Dark Matter)
Originally Answered: If light reaches the Earth from the sun, why is the space between the sun and the Earth dark? Because light illuminates surfaces, objects. Space is not an object, is the lack of matter. If you turn on a flashlight in a dark room you will illuminate the floors and the walls...- angela
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Dark matter Light Matter
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
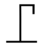
I How does the magnetic component of an EM wave affect surroundings?
Hi all, as we all know EM waves are made up of magnetic and electric waves in a plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation. Given this, why don't I see conductors being affected when I shine light at them? Woulnt the magnetism cause a force? Is is that the force is too small? What am i...- Boltzman Oscillation
- Thread
- Replies: 8
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
J
B Basic confusion about the Big Bang and light cones
I’m getting confused somewhere, and I’d be obliged if someone could pinpoint my error. 1. At or near the Big Bang, everything was so close as to be within each other’s light cones. 2. All parts of the cosmos are now outside of some other parts’ light cones. Therefore, 3. Something traveled...- Joseph Flatt
- Thread
- Replies: 11
- Forum: Cosmology
-
M
I Measuring Light Reflection in a Black Hole
To keep things "simple", the black hole is 1E30 kilograms. The statite (stationary satellite, blue) hovers above the hole at a fixed location (twice the Schwarzschild radius from the singularity) by tremendous acceleration. The statite drops a probe (green) that begins to fall toward the hole at...- Mike S.
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Black hole Falling Hole Light
- Replies: 89
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
P
I What if the Universe expands faster than the speed of light?
I may be way off, but at some point in the past I understand there was super expansion where the universe expanded faster than the speed of light. If matter expanded with it it's an example of matter in separate areas moving apart faster than the speed of light. If it didn't the universe has...- peterraymond
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Light Speed Speed of light Universe
- Replies: 19
- Forum: Cosmology
-

B In what way does light behave that is incompatible with waves?
Waves are energy moving. Light is moving packets of fixed amounts of energy. Why must we invoke particles to understand light? How is a wave (energy moving) antithetical to packets of energy?- Ray McDavis
- Thread
- Replies: 12
- Forum: Quantum Physics
-
B Is light breaking its own speed limit when cornering?
Being a neophyte to physics, I try to visualize a light cone as it travels about. I try to put myself in it and use my car to talk of it. When I ride in my my car, I note that when I corner, one wheel will speed up as compared to the other side. A light cone does the same, and given that the... -

Star Trek the Next Generation - The Inner Light
I just watched this episode of Star Trek the Next Generation; The Inner Light. One of my favorites. edit: I just found this from a google search- dlgoff
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Generation Light Star Star trek
- Replies: 3
- Forum: Science Fiction and Fantasy Media
-
G
I Collimating a fibre-coupled LED light source
Summary:: I have a fibre coupled LED light and an achromatic doublet lens, I know by placing the collimating lens at a distance equal to the focal length of the lens, the light will get collimated. But is the a simulation software available where I can input the parameters I can so as to... -
R
I Black Hole Waterfall Analogy & Light Speed
Recently I have seen a number of General Relativity visualisations that show spacetime flowing towards any mass, similar to water flowing into a sink hole. ScienceClic's video is an example. That model is also used in the "waterfall model" to explain the event horizon of a black hole, as the...- Rene Dekker
- Thread
- Replies: 15
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Why is Light Speed Invariant & Finite?
I think infinite speed is unimaginable. If something is moving at infinite speed, we can't find it at all because it has moved to infinity. Furthermore, when the maximum speed is limited, a reasonable inference should be that observers in different reference frames should find the same one speed...- alan123hk
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Why is the speed of light a constant?
The question is of what does it depend on? We take it for a constant still how do we know that its the exactly the same as in a vacuum in a center or closer to the center of our galaxy for example. Why is the number what it is?- Mohika
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Constant Light Speed Speed of light
- Replies: 34
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
L
Light incident on a sphere, focused at a distance ##2R##
I used the equation for the refraction on a spherical surface: ##\frac{n_1}{p}+\frac{n_2}{q}=\frac{n_2-n_1}{R}##, where ##n_1=1## is the index of refraction of air, ##n_2## the index of refraction of the sphere, ##R## is the radius of the glass sphere, ##p## is the object distance which, since...- lorenz0
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
M
B Measuring Light Velocity Correctly: Thought Experiment
Let there be a track 450,000 km long and a rocket 300,000 km long with a laser attached to the bottom of it's back end with a clock beside it, and a second synchronized clock attached to bottom of its front end. Both clocks were also synchronized with a track clock while the rocket was parked...- Magatron
- Thread
- Replies: 28
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
D
I Light Speed in Dense Medium: Explained
If light goes from air through glass, the reason the light bends is because I'm told that the light travels slower inside the glass. If I change my observer reference to inside the glass, the speed of light inside the medium it look like light is still traveling at the speed of light? if so, the...- deedee6905
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Light Medium Speed Speed of light
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
E
I Why Do Longer Wavelengths Go Slower in Glass?
I reviewed the derivation / solution of that GRT problem and do not see any dependence on the wavelength of the light. Is that correct, or am I missing something? This makes me wonder about my understanding of how prisms work. How or why do longer wavelengths go slower in glass than shorter...- exmarine
- Thread
- Replies: 9
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

B Question regarding light from distant objects
Given that the universe is expanding, and we currently believe the universe as we know it began a little over 13 billion years ago, Then when we look at a distant object and say we are looking light from 10 billion years ago, How is that possible. With the universe expanding for 13 billion... -
B
Does light passed through two window screens get polarized?
If you take two window screens and hold them, say, a couple feet apart and look through both of them, you see what looks like interference patterns. These types of patterns can also be seen in transparent materials when polarized light is passed through them. More on stressed materials and... -
S
I Why does light travel slower in water?
I always thought it was from individual water molecules absorbing and reabsorbing light, but this explanation in a video from Fermilab is very strange to me . What is this "new wave" he speaks of; wouldn't it be light too? If so, then this light is now slower than the speed of light, which...- student34
- Thread
- Replies: 31
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
L
A Energy problem of light interference
During equal thickness interference, adjust the inclination of the two plates to expand the spacing of interference fringes to 10mm. Then, if a light with a width of 5mm is used for equal thickness interference, whether an interference pattern will be observed, and the width of the interference...- liuxinhua
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Classical Physics
-

I How is light modeled in astrophysics?
Suppose a light beam is sent from a distant star. When the light beam hit a telescope orbiting around the Earth. How is the light beam modeled? I have searched for many keywords without success. In my opinion, since the beam has gone so far, it can be viewed as parallel rays, with a decaying...- Haorong Wu
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Astrophysics Light
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-
D
Optical Where to look for a UV light that is invisible to the naked eye?
Where to look for a UV light that is invisible to the naked eye? Essentially I want to buy a UV light that doesn't have that annoying blue glow, I just want the UV light that is invisible to the naked eye like infrared light. I read a bit about it and from what I read what I'm looking for is...- David Nolan
- Thread
- Replies: 13
- Forum: DIY Projects
-

B Is there a material that allows visible light and UV light to pass through?
Is there a material that allows visible light and uv light to pass through? Edit: A physical material -
I Does light escape the Universe?
Googleing this question yields answers that don't really seem to address the core of my question. I apologize if I just haven't been able to see how answers are applicable, and would greatly appreciate any insight. Imagine a universe consisting of only our sun. no planets, no galaxies...- swankdave
- Thread
- Replies: 1
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
G
B What experiments confirmed the constant velocity of light?
What other experiments, besides the M&M experiments confirmed the constant velocity of light? Thank you in advance for the response.- Grampa Dee
- Thread
- Replies: 42
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-
G
To find the modulus of elasticity of a light elastic string
Could I please ask for help with the following question? Four uniform rods of equal length l and weight w are freely jointed to form a framework ABCD. The joints A and C are connected by a light elastic string of natural length a. The framework is freely suspended from A and takes up the shape...- gnits
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

How does the "CLEAN" light on a coffeemaker work?
My Cuisinart drip coffee maker has a light that comes on, telling you to run it through a cleaning cycle (50/50 mix water/vinegar, rinse). In our previous home, we were on a well of about 750 ppm dissolved solids (including some iron), so I had an RO unit connected after the water softener to...- NTL2009
- Thread
- Replies: 3
- Forum: General Engineering
-

I Do Photons Attract Each Other?
Then the equation of motion for a photon in the beam (moving parallel to the ##x## axis) is\begin{align*} \ddot{y} = - \Gamma^y_{\mu \nu} \dot{x}^{\mu} \dot{x}^{\nu} = -[\Gamma^y_{00} + \Gamma^y_{xx} + 2\Gamma^y_{0x}](\dot{x}^0)^2 \end{align*}and similar for ##z##. In the linearised theory...- ergospherical
- Thread
- Replies: 7
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Energy Flow From Battery to the Light Bulb
When we connect tungsten filament light bulb to the battery, filament becomes hot due to electrons losing kinetic energy in the electric field inside of conductor. Heat is eventually converted to electromagnetic radiation making light bulb shine. Light energy comes from flow of electrons and...- Dario56
- Thread
- Replies: 16
- Forum: Classical Physics
-
D
Magnitude and average value of energy intensity of light beam
I tried using the equations above, but I wasn't really able to come up with an intuitive explanation. From my understanding, the electric field vector only varies in the x-y plane while the magnetic field vector only varies in the z-y plane. Also, both vary sinusoidally and both reach extrema...- dl447342
- Thread
- Replies: 10
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
O
I Umbrella fabric and diffraction pattern
It is sometimes said that a distant street lamp seen through a dark coloured umbrella fabric appears like dotted diffraction pattern, as in figure A. However, I have tried several umbrellas but all of them produce a blurred cross, as in figure B. The umbrella fabric superficially looks like a...- Orthoceras
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Optics
-
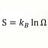
B One way speed of light in one reference frame measurement
Two clocks with photo detectors are 100 kilometers apart at A and B. On the center of AB axis two light pulses are sent to the clocks , synchronizing them. Then a light signal is sent from A to B. The two stationary observers record the time from event at A to event at B. Is there a one way...- morrobay
- Thread
- Replies: 5
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-
J
I Using Diffraction (i.e., Fresnel Zone Plate) to defocus/diverge light
I am wondering if it is possible to use principals of diffraction to cause a collimated beam of light (laser) to become divergent. I see that zone plates are most always used for focusing the light from a source, unless they are used in reverse. This is why zone plates are seemingly always...- jgk5141
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Other Physics Topics
-

B Finding One-Way Speed of Light: Use One Clock
First off, I'm probably totally incorrect on all of this, so feel free to correct me. Second, I'm only 15, so please just be gentle and helpful when I'm totally off. Now for my idea: Have a huge vacuum and put lasers on the inside with hundreds of different lasers at different angles equally...- TylerSmith
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Clock Idea Light Speed Speed of light
- Replies: 14
- Forum: Special and General Relativity
-

I Exploring the Speed of Light: Gravitational Waves
Why are gravitational waves able to move at the speed of light?- brucegoth123
- Thread
- Replies: 2
- Forum: Astronomy and Astrophysics
-

Inside glass, can I apply relativity of speed for light?
I was doing a exercise which considerst he time it takes for light travels a glass with thickness proper D and velocity v. The speed of light is c/n inside the glass. Now, my approach was to go to the glass frame, take the relative speed between the glass and the light using the trivial formula...- LCSphysicist
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Apply Glass Light Relativity Speed
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help
-

[HW question] Image size difference of two light emitting nanospheres
I wonder if this question is about two-point resolution or magnification... Would someone here be so kind as to offer some guidance on this question? Thank you!- rinalai
- Thread
-
- Tags
- Difference Image Light
- Replies: 4
- Forum: Introductory Physics Homework Help