- #1
tomeatworld
- 51
- 0
Firstly, sorry if this is in the wrong section. I'll happily move it if it should be somewhere else.
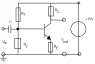
What is the impedence between the base of the BJT and ground of the common emitter amplifier circuit.
Ic = IE
So I started by saying that [tex]\Delta[/tex]Vb = [tex]\Delta[/tex]IE RE and that [tex]\Delta[/tex]IE = [tex]\Delta[/tex]IB hfe where hfe is the gain of the circuit. By then equating the two using [tex]\Delta[/tex]IE I find that [tex]\Delta[/tex]IB = [tex]\frac{\Delta V_{B}}{R_{E}h_{fe}}[/tex] so impedence is REhfe but this seems very simple considering the circuit. Am I missing anything?
Homework Statement
What is the impedence between the base of the BJT and ground of the common emitter amplifier circuit.
Homework Equations
Ic = IE
The Attempt at a Solution
So I started by saying that [tex]\Delta[/tex]Vb = [tex]\Delta[/tex]IE RE and that [tex]\Delta[/tex]IE = [tex]\Delta[/tex]IB hfe where hfe is the gain of the circuit. By then equating the two using [tex]\Delta[/tex]IE I find that [tex]\Delta[/tex]IB = [tex]\frac{\Delta V_{B}}{R_{E}h_{fe}}[/tex] so impedence is REhfe but this seems very simple considering the circuit. Am I missing anything?