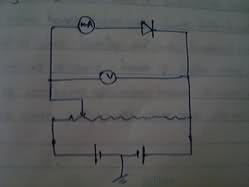
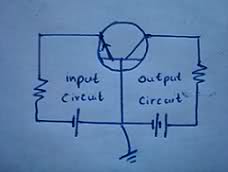
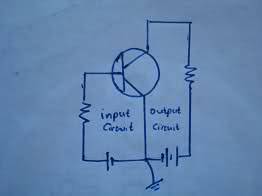
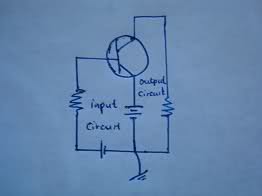
Grounding in circuits serves multiple purposes, including providing a common reference point for voltage measurements, enhancing safety by preventing shock hazards, and reducing electromagnetic noise. Not all grounds are connected to the Earth; some may connect to a chassis or represent a common power supply rail. Grounding can also facilitate the design of circuit diagrams by simplifying connections and avoiding clutter. In sensitive circuits, grounding is crucial for noise suppression and maintaining consistent potentials. Understanding grounding is essential for effective circuit design and operation, particularly in complex systems.