kmarinas86
- 974
- 1
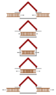
kmarinas86 said:Figure 4: Scenario in the garage frame: a length contracted ladder entering and exiting the garage
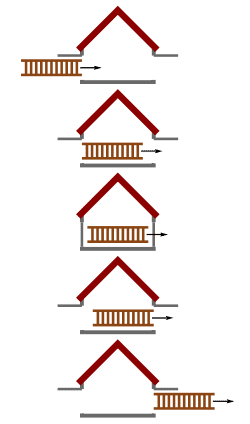
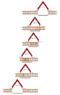
Figure 5: Scenario in the ladder frame: a length contracted garage passing over the ladder

So what happens if we have TWO ladders moving in opposite directions through the same garage?
Figure 4: Scenario in the garage frame: a length contracted ladder entering and exiting the garage
Figure 5: Scenario in the ladder frame: a length contracted garage passing over the ladder
Something's amiss.
How, in the last diagram, does the second ladder (the one faster than garage) spend LESS time inside the garage so that (unlike as depicted in the last diagram) the faster ladder doesn't hit the doors of the garage.
Attachments
Last edited: