evinda
Gold Member
MHB
- 3,741
- 0
Hello! (Wave)
I want to apply the algorithm of the depth-first search at an example.
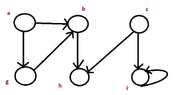
This is the example,at which I want to apply the algorithm:
View attachment 3064
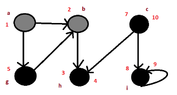
According to my notes,it is like that:
View attachment 3066
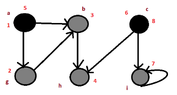
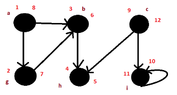
but..I found the following:
View attachment 3067
Could you tell me which of them is right? Have I done something wrong? (Thinking)
I want to apply the algorithm of the depth-first search at an example.
Code:
Depthfirstsearch(G)
for each v ∈ V
color[v]<-white
p[v]<-Ø
time<-Ø
for each u ∈ V
if color[u]=white then
Visit(u)
Code:
Visit(u)
color[u]<-gray
time<-time+1
d[u]<-time
for each v ∈ Adj[u]
if color[v]=white then
p[v]<-u
Visit(v)
color[u]<-black
time<-time+1
f[u]<-timeThis is the example,at which I want to apply the algorithm:
View attachment 3064
According to my notes,it is like that:
View attachment 3066
but..I found the following:
View attachment 3067
Could you tell me which of them is right? Have I done something wrong? (Thinking)