BosonF
Homework Statement
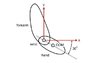
When the hand is rotating about the wrist in the sagittal plane its centre of mass has an acceleration of 3m/s(squared) in a horizontal direction, its mass is 2kg and the vertical direction (i.e. Y) is against gravity. The hand travels through 30 degrees. If the distance from the wrist joint to the centre of mass is 0.04m, what should the angular acceleration of the hand about the wrist be?
a) 17.5
b) 27.5
c) 37.5
d) 47.5
Homework Equations
angular acceleration = change in angular velocity/time
The Attempt at a Solution
To calculate the time I made an assumption that the starting velocity was 0 and the ending velocity was 3m//s. I converted the degrees to radians by multiplying by pi/180. To calculate the distance traveled in the x direction I used x= Cos30 x 0.04. So if the hand travels 3m in 1s then it travels xm in x/3 s. Which worked out as 0.034641/3 = 0.01155s.
To find the angular acceleration I then divided the radians by the time. which gave me 0.5236-0/0.01155 = 45.33 rad/s(squared)
Have I followed the correct method?