vatuhiva
- 3
- 0
- TL;DR
- Calculating the normal force in the bearing pads of a thrust-bearing due to axial and moment loads.
Hello all!
I have a mathematical question for you. I'm trying to design a thrust bearing that can withstand axial and moment loads. I've added a picture of a similar design. The design consists of two rings (grey) and sliding pads (blue) fixed on the bottom ring. The top ring slides over the blue pads. The blue pads are made of an plastic with a low coefficient of friction. I would like to calculate the required force needed for the bearing to turn. therefore I need to know the force acting on the individual pads. I would also like to check whether the pressure on the individual pads will be acceptable.
The axial load will need to be large enough to keep the bearing in place. But once that is the case the moment load will put an extra force on the pads on the right side of the bearing and relieve the pads on the left. I trying to find any formula's that could help me solve this issue but sofar I haven't been able to find suitable information regarding this issue.
I hope there are people out there that can help me a bit further! I there are any question I will be happy to answer those!
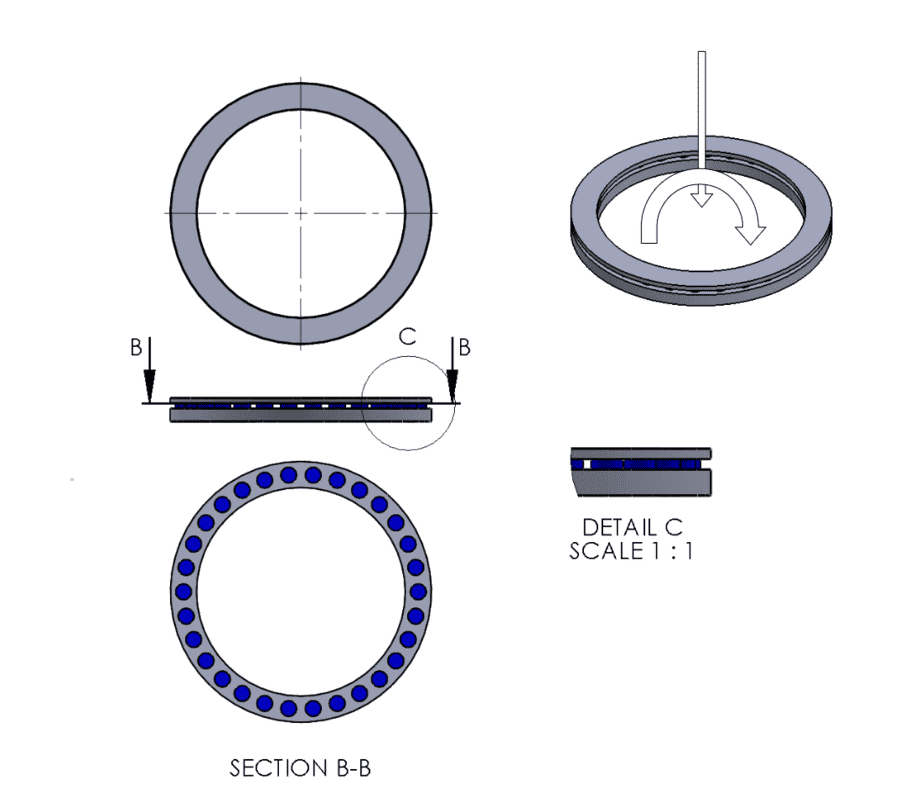
I have a mathematical question for you. I'm trying to design a thrust bearing that can withstand axial and moment loads. I've added a picture of a similar design. The design consists of two rings (grey) and sliding pads (blue) fixed on the bottom ring. The top ring slides over the blue pads. The blue pads are made of an plastic with a low coefficient of friction. I would like to calculate the required force needed for the bearing to turn. therefore I need to know the force acting on the individual pads. I would also like to check whether the pressure on the individual pads will be acceptable.
The axial load will need to be large enough to keep the bearing in place. But once that is the case the moment load will put an extra force on the pads on the right side of the bearing and relieve the pads on the left. I trying to find any formula's that could help me solve this issue but sofar I haven't been able to find suitable information regarding this issue.
I hope there are people out there that can help me a bit further! I there are any question I will be happy to answer those!