- #1
TxAggie00
- 4
- 0
Hello All!
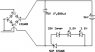
I have a question about negative switching for a capacitor dump circuit. Currently we are dumping a capacitor to 3 12VDC battery on the negative leg. We are using an SCR, 5.1V zener and two 3.2V LEDS. The capacitor is a 75V, 17,000 uF computer grade cap. The capacitor charges up to the battery voltage + the zener + the 2 LEDS (~48V - 50V) then dumps. We have some problems with the SCR "latching" and was told there was a better way using a FET. The problem is I am somewhat clueless on how that can be done. Anyone have any ideas?
Thanks,
Scott
Note: ignore the 33V zener in the attached picture. It is a 5.1V zener
I have a question about negative switching for a capacitor dump circuit. Currently we are dumping a capacitor to 3 12VDC battery on the negative leg. We are using an SCR, 5.1V zener and two 3.2V LEDS. The capacitor is a 75V, 17,000 uF computer grade cap. The capacitor charges up to the battery voltage + the zener + the 2 LEDS (~48V - 50V) then dumps. We have some problems with the SCR "latching" and was told there was a better way using a FET. The problem is I am somewhat clueless on how that can be done. Anyone have any ideas?
Thanks,
Scott
Note: ignore the 33V zener in the attached picture. It is a 5.1V zener