L_landau
- 27
- 0
Homework Statement
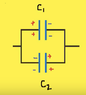
Capacitors C1 = 6.97 uF and C2 = 1.54 uF are charged as a parallel combination across a 281 V battery. The capacitors are disconnected from the battery and from each other. They are then connected positive plate to negative plate and negative plate to positive plate.
A) Calculate the resulting charge on capacitor C1.
B) Calculate the resulting charge on capacitor C2.
from this answer
http://www.chegg.com/homework-help/questions-and-answers/capacitors-c1-697-uf-c2-154-uf-charged-parallel-combination-across-281-v-battery-capacitor-q1385340
Homework Equations
Q = CΔV
The Attempt at a Solution
So q1 = 1.5x10-3c and q2 = 5x10-4c. Why would the drawing show opposite polarizations on the plates? Shouldn't the battery give the same potential drop across two capacitors in parallel?