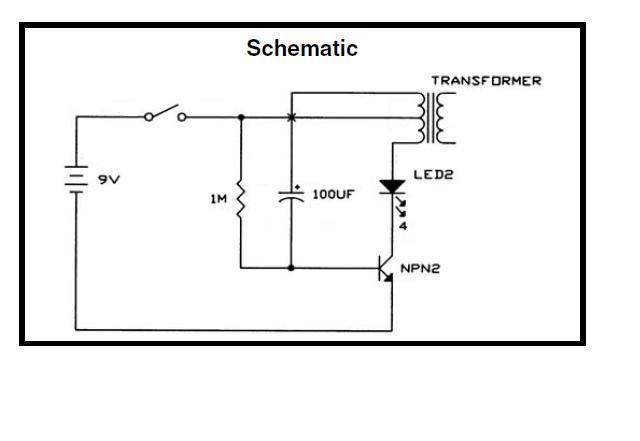
The Lighthouse Circuit operates by charging a capacitor when a voltage source is applied, which in turn activates a transistor to power an LED. As the capacitor charges, it eventually triggers the transistor, allowing current to flow to the LED, causing it to light up. The resistor plays a crucial role in controlling the charge and discharge rate of the capacitor, while the transformer may be involved in stepping up or down voltage levels as needed. Once the capacitor discharges below a certain threshold, the LED turns off, and the cycle repeats. This interaction between the capacitor, resistor, transistor, and potentially the transformer creates a timing mechanism within the circuit.
 It would be a great help! Thanks in advance!
It would be a great help! Thanks in advance!