SUMMARY
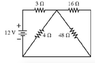
The discussion centers on calculating the current and potential difference through a 3Ω resistor in a circuit containing multiple resistors, specifically 4Ω, 16Ω, and 48Ω. Participants emphasize the importance of simplifying the circuit by identifying parallel resistors, particularly the 4Ω and 48Ω resistors, to calculate the equivalent resistance (Req) using the formula Req = (1/R1 + 1/R2 +...) -1. Establishing the equivalent resistance allows for straightforward calculations of current and voltage across the resistors, which is crucial for solving the problem effectively.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Ohm's Law and Kirchhoff's Voltage Law
- Familiarity with series and parallel resistor configurations
- Ability to calculate equivalent resistance in circuits
- Basic circuit diagram drawing skills
NEXT STEPS
- Learn how to calculate equivalent resistance for complex resistor networks
- Study Kirchhoff's Laws in greater detail for circuit analysis
- Practice drawing and simplifying circuit diagrams for clarity
- Explore the implications of voltage division in series circuits
USEFUL FOR
Students studying electrical engineering, circuit designers, and anyone looking to improve their skills in circuit analysis and resistor calculations.