- #1
BuckeyeNut
- 1
- 0
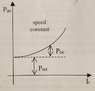
I am trying to understand this curve; it is AC Power vs. Field Current of a DC Generator. I am not sure what its significance is? What it's telling me? Can someone please explain it to me? See attached image.
BTW... Pac = AC Power
If = field current
Poc = open circuit power
Prot = rotational power (I believe)
Thanks in advance!
BTW... Pac = AC Power
If = field current
Poc = open circuit power
Prot = rotational power (I believe)
Thanks in advance!