lba
- 43
- 0
Hi ;)
I'm new on the forum
I have a question in fluid mechanics:
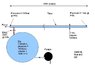
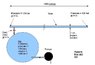
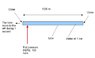
A tube of length 1500 meters has water inside at 1 bar of pressure.
A time t=0s we put 100 bars of pressure in a side close to the left end of the tube. The pressure will be at the other side at time t=1s because it's the speed of sound in water. So, an end of the tube has 100 bars and another end has 1 bar. The tube move to the left during 1 second. If the tube move it can give energy. Where come from this energy ? Put pressure in the tube can be recover because pressure it's only potential energy, so after 1s we can depress at right the tube and recover energy (in this case the tube move to left again...). If someone can explain to me ?
Thanks
I'm new on the forum
I have a question in fluid mechanics:
A tube of length 1500 meters has water inside at 1 bar of pressure.
A time t=0s we put 100 bars of pressure in a side close to the left end of the tube. The pressure will be at the other side at time t=1s because it's the speed of sound in water. So, an end of the tube has 100 bars and another end has 1 bar. The tube move to the left during 1 second. If the tube move it can give energy. Where come from this energy ? Put pressure in the tube can be recover because pressure it's only potential energy, so after 1s we can depress at right the tube and recover energy (in this case the tube move to left again...). If someone can explain to me ?
Thanks
Attachments
Last edited: