- #1
AmazingTrans
- 8
- 0
I am doing this as a hobby, trying to understanding some physics calculation for camshafts and following cam s,v,a,j.
All pictures in this thread are just samples that tie to nothing much, other than just images.
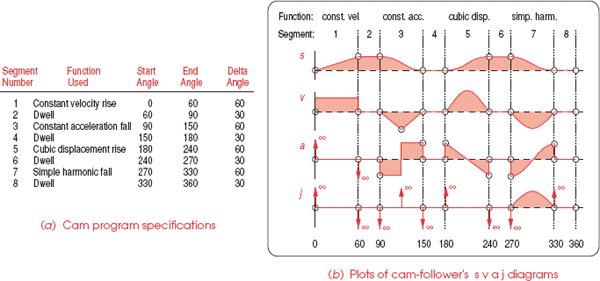
1. From the 1st image above, the camshaft (emulated digital signal) is moving at a "constant speed", and the follower (motor) has the following plot. The camshaft has no boundaries in terms of velocity, acceleration, or jerk since it is digitally emulated.
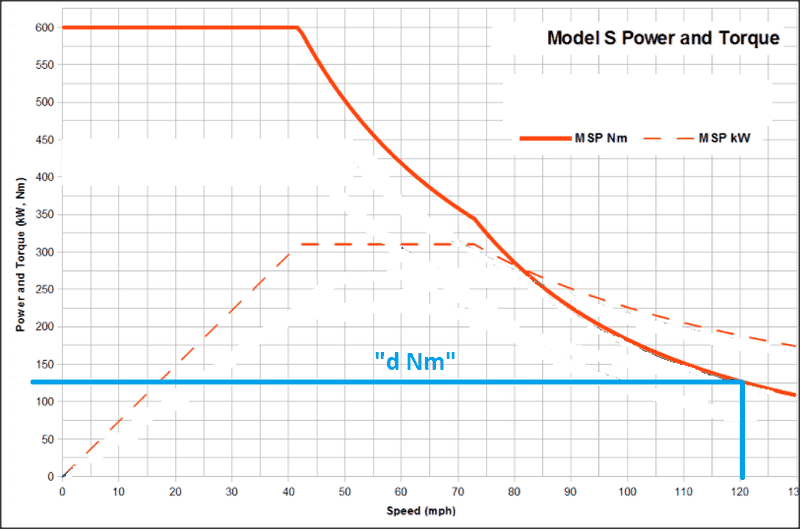
I also have included the follower (which is a motor) properties. (Yes that's a tesla S motor. =D ) As we can see, the higher the speed of the motor, the lesser torque.
If the follower/motor is running at 120 mph and only capable of "d Nm" (reduced torque),
At point #2 of the cam plot and the camshaft decided to stop at a specific rate "x".
What would the camshaft deceleration formula look like if I want the follower/motor to not exceed 75% of the torque curve at that point ?
My goal here is to use to constantly change the camshaft deceleration rate such that the follower does not ride along its torque curve all the time.
All pictures in this thread are just samples that tie to nothing much, other than just images.
1. From the 1st image above, the camshaft (emulated digital signal) is moving at a "constant speed", and the follower (motor) has the following plot. The camshaft has no boundaries in terms of velocity, acceleration, or jerk since it is digitally emulated.
I also have included the follower (which is a motor) properties. (Yes that's a tesla S motor. =D ) As we can see, the higher the speed of the motor, the lesser torque.
If the follower/motor is running at 120 mph and only capable of "d Nm" (reduced torque),
At point #2 of the cam plot and the camshaft decided to stop at a specific rate "x".
What would the camshaft deceleration formula look like if I want the follower/motor to not exceed 75% of the torque curve at that point ?
My goal here is to use to constantly change the camshaft deceleration rate such that the follower does not ride along its torque curve all the time.