- #1
Inquiring_M
- 1
- 0
Hello all !
I have the following problem.
I have to calculate the DTFT of this : x(n)=u(n)-u(n-4).
Fourier Transformations
So far , from what I have studied I have understood, that a DTFT , is actually many DFT's calculated for different omega values, let's say in an interval from -pi to pi , with step 0.2 .
Is this alright so far ?
It is proven that x[n] = 1
So finally have this:
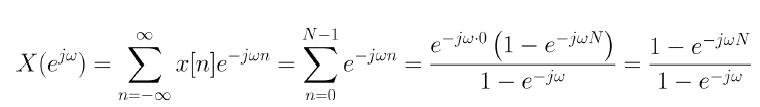
Now my main problem, how can I continue from that step ? Am I supposed to get some arithmetic result ?
Thanks for you help !
Homework Statement
I have the following problem.
I have to calculate the DTFT of this : x(n)=u(n)-u(n-4).
Homework Equations
Fourier Transformations
The Attempt at a Solution
So far , from what I have studied I have understood, that a DTFT , is actually many DFT's calculated for different omega values, let's say in an interval from -pi to pi , with step 0.2 .
Is this alright so far ?
It is proven that x[n] = 1
So finally have this:
Now my main problem, how can I continue from that step ? Am I supposed to get some arithmetic result ?
Thanks for you help !