pb23me
- 204
- 0
Homework Statement
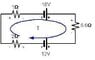
determine the terminal voltage in each battery.
Emf1=18V
r1=1 ohm
EMF2=12V
r2=2 ohm
R=6.6 ohms
also the batterys currents are opposing each other.
Homework Equations
Vab=emf-IrThe Attempt at a Solution
i used kirchnoffs rule to find the current I , 18-I6.6-12-I2-I=0 and got I= .625 then i thought i would just use Vab=emf-Ir to find the terminal voltage of each battery however I am not getting the correct answer... could someone please explain this to me i have a test tomorrow morning and i really need to figure this out! the answers i got were 17.375 for the 18V batt and 10.75 for the 12V battAttachments
Last edited: