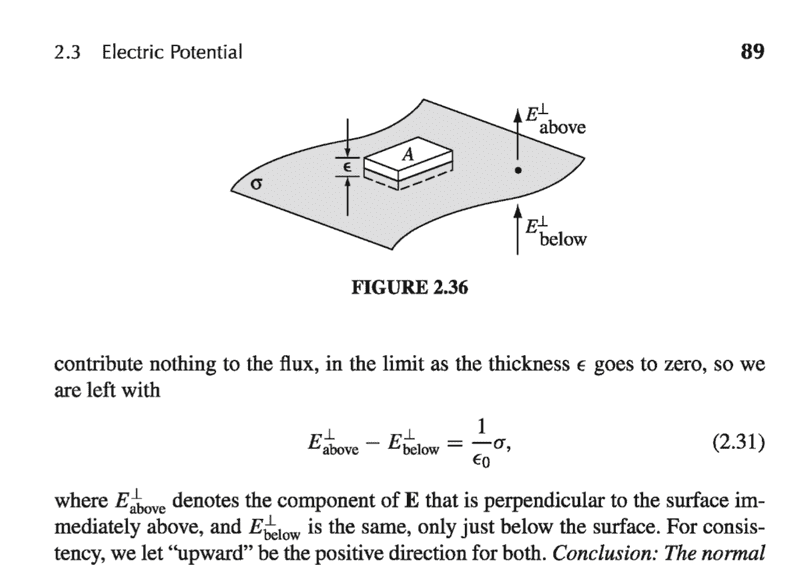
The discussion centers on understanding the behavior of the electric field across a surface charge, particularly using a pillbox Gaussian surface. The key point is that the electric field can point in the same direction on both sides of the surface, depending on the configuration. Two examples illustrate this: in the first, a single charged surface creates an upward field above and a downward field below, while in the second, a charged surface placed between capacitor plates results in an upward field on both sides. The importance of maintaining a consistent sign convention is emphasized, which affects the calculations involving the electric field difference and leads to the application of Gauss's law. The conversation also highlights the usefulness of prior discussions and resources, such as Jackson's book, for clarifying these concepts.