SUMMARY
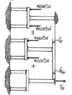
The discussion centers on calculating average normal stress in a rod using Newton's 2nd Law. The user questions the treatment of forces in the problem, specifically why a single 40 kN force is considered for delta P while delta EF uses an F/2 approach. The user proposes an alternative solution involving specific formulas for force calculations based on rod dimensions and material properties, ultimately arriving at a displacement of 0.0874 mm and forces of 38,380 N and 20,810 N, which do not match the book's answer.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Newton's 2nd Law
- Knowledge of stress and strain calculations
- Familiarity with basic mechanics of materials
- Ability to perform calculations involving cross-sectional areas and material properties
NEXT STEPS
- Review calculations for average normal stress in rods
- Study the application of Newton's 2nd Law in static equilibrium problems
- Explore the derivation of force equations for different cross-sectional areas
- Investigate discrepancies in textbook solutions and common pitfalls in mechanics problems
USEFUL FOR
This discussion is beneficial for engineering students, mechanics instructors, and professionals in structural engineering who are focused on understanding stress analysis in materials.