- #1
meaghan
- 15
- 1
Homework Statement
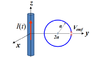
I have a circular loop with a radius of 1 m. The center of the loop is located 2 m away from a infinitely long current carrying wire, with ac current I. Find the flux in the circular loop
Homework Equations
Φ = ∫ B ds
The Attempt at a Solution
I've found a lot of examples with square loops, so the magnetic field in the loop will depend on both the x and y direction.
I got that Φ = ∫ uo I / π(2+y) *√(1-y2) since the magnetic field will change according to the point on the circle.