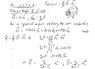jegues
- 1,085
- 3
Homework Statement
A coaxial transmission line has an inner conducting cylinder of radius a and an outer conducting cylinder of radius c. Charge ql per unit length is uniformly distributed over the inner conductor and -ql over the outer. If dielectric \epsilon_{1} extends from r=a to r=b and dielectric \epsilon_{2} from r=b r=c, find the electric field for r<a, for a<r<b, for b<r<c and for r>c. Take the conducting cylinders as infinitesimally thin.
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
For r<a there is no charge enclosed thus the flux is 0 so E is also 0
Here is the solution they give for a<r<b. (see figure attached)
I am confused as to how he determines the components of the vector d\vec{S}. Is there a picture that will explain this?
Thanks again!