Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around calculating the pressure in each cylinder of a four-stroke engine at various crank angles. Participants explore the complexities involved in creating a flexible formula that accounts for multiple variables affecting cylinder pressure, including piston offset, valve timing, and engine configuration.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- One participant expresses frustration in creating a spreadsheet to calculate cylinder pressure for multiple cylinders based on crank angle, seeking a single function for this purpose.
- Another participant asserts that no equation exists for pressure based solely on crank angle due to the involvement of additional variables like piston offset.
- Some participants propose that if the forcing profile is the same, cylinder pressures can be phased according to firing order, but question the feasibility of a universal equation that applies to all engines.
- One participant mentions the need to factor in variables such as valve timing and air flow, suggesting that the precision of any equation would depend on how many variables are included.
- Another participant challenges the idea of a single function, arguing that calculating pressures at different crank angles does not equate to a single equation for all engines.
- Some participants discuss the implications of inertia and friction on the torque profile and whether these factors are considered in the current model.
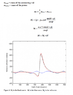
- One participant shares a series of conditional statements they developed to calculate cylinder pressure across different crank angles, indicating progress in their modeling efforts.
- There is mention of the need to distort the pressure-volume (p-V) diagram based on peak torque RPMs, with acknowledgment that this aspect complicates the calculations further.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the possibility of a single equation for calculating cylinder pressure across multiple cylinders. While some agree on the need for a more complex model that incorporates various factors, others maintain that a straightforward phasing of calculations can be achieved. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the existence of a universal formula applicable to all engine types.
Contextual Notes
Participants highlight limitations in their discussions, including the dependence on specific engine configurations, the complexity of variables involved, and the challenges in achieving a universally applicable equation for cylinder pressure calculations.