SUMMARY
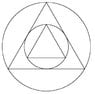
The discussion centers on calculating the sum of areas for an infinite series of circles and triangles based on a given geometric figure. The largest circle has a radius of 10, leading to a calculated area of 475/3 π for the circles and 175/2 √3 for the triangles. The geometric series formula is applied to derive the area of the circles, confirming the use of the first term as 10² and the second term as 5², with a common ratio of 1/4. The calculations are validated through the cosine law and Pythagorean theorem, ensuring the correctness of the derived formulas.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of geometric series and their convergence
- Knowledge of the cosine law in triangle geometry
- Familiarity with the Pythagorean theorem
- Basic skills in manipulating algebraic expressions involving π and square roots
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of geometric series sums in calculus
- Explore advanced applications of the cosine law in various geometric configurations
- Learn about the properties of infinite series and their convergence criteria
- Investigate the relationship between circles and triangles in geometric constructions
USEFUL FOR
Students and educators in geometry, mathematicians focusing on series and geometric properties, and anyone involved in solving complex geometric problems.