- #1
Viroos
- 4
- 0
Hi !
I have very basic question about gyroscopes: do I need same torque from gimbal motor to accelerate the flywheel whenever it's rotating or not ? (and the gimbal motor is attached to the floor)
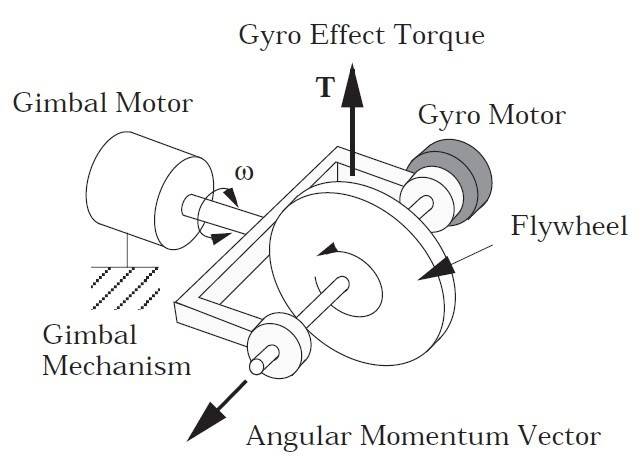
Thanks in advance :)
I have very basic question about gyroscopes: do I need same torque from gimbal motor to accelerate the flywheel whenever it's rotating or not ? (and the gimbal motor is attached to the floor)
Thanks in advance :)