- #1
Carlos de Meo
- 23
- 2
Hi Guys
I´m studying the heat exchange problem in furnaces and, to begin with, i started with Incropera´s book.
One thing is actually driving me crazy
On the last part of this exercise´s solution (part 3), the physical principle involved is not very clear to me. To calculate the absorptivity of the wall, it´s assumed that emissivity = absorptivity. But, as far as i know, this is the famous Kirchhoff Law and it´s only valid when the system reaches thermal equilibrium, which is clearly not the case here. Can someone explain me what is going on?
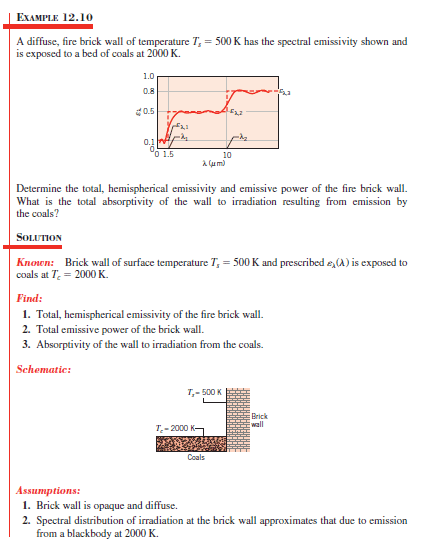

I´m studying the heat exchange problem in furnaces and, to begin with, i started with Incropera´s book.
One thing is actually driving me crazy
On the last part of this exercise´s solution (part 3), the physical principle involved is not very clear to me. To calculate the absorptivity of the wall, it´s assumed that emissivity = absorptivity. But, as far as i know, this is the famous Kirchhoff Law and it´s only valid when the system reaches thermal equilibrium, which is clearly not the case here. Can someone explain me what is going on?