You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
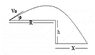
Help with a very easy mechanic problem. (Still I can´t solve it)
- Thread starter mprm86
- Start date
-
- Tags
- Mechanic
AI Thread Summary
To minimize the distance X in the projectile problem, the choice of initial velocity (Vo) and angle (Theta) is crucial. The distance X is minimized when the projectile just misses the edge of the table, which requires analyzing the trajectory as a parabolic function. The optimal angle Theta should be determined based on the relationship between Vo and the horizontal distance R, with the equation R = 2Vo^2(sin(Theta)cos(Theta)/g) guiding the calculations. The minimum distance occurs when the projectile's vertical speed is maximized at the edge of the table, leading to a specific relationship between Vo and Theta. Ultimately, the problem emphasizes finding the right combination of these variables to achieve the desired outcome.
Physics news on Phys.org
tnorkhangpa
- 6
- 0
See, x will be minimum if the projectile(assuming it is a point- object) just crosses the edge of the table. Just try to equate the range,(R)
R = 2v^2(sin(theta)cos(theta)/ g
You know the value of R(which is given in the question). Just use that and you will know the value of theta and initial velocity.
R = 2v^2(sin(theta)cos(theta)/ g
You know the value of R(which is given in the question). Just use that and you will know the value of theta and initial velocity.
mprm86
- 52
- 0
The problem is for any initial velocity, not for an specific one. It is also for any value of Theta. The problem here is to see how should we choose theta and Vo, for making the distance x as minimum as possible.
I guess that if we chooose that Vo be the maximum it can be, so the height it reaches will be also maximum for values of theta near to 90. The problem here is, which should be the exact value of theta, when Vo is maximum, in order to making the distance x the minimum.
I guess that if we chooose that Vo be the maximum it can be, so the height it reaches will be also maximum for values of theta near to 90. The problem here is, which should be the exact value of theta, when Vo is maximum, in order to making the distance x the minimum.
dextercioby
Science Advisor
- 13,388
- 4,040
Okay then,so you've got the function R(v_{0},\theta) which needs to be minimized.Okay,then treat is as a maths problem in which you've got to find out the values for extremum for a 2-variable function.
Set the PD wrt the variables equal to 0,then find the values for extremum and then compute the hessian on these solutions.It should be >0,for a minimum.
Daniel.
Set the PD wrt the variables equal to 0,then find the values for extremum and then compute the hessian on these solutions.It should be >0,for a minimum.
Daniel.
Andrew Mason
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 7,794
- 502
The trajectory is a parabola. So the drawing is not accurate.mprm86 said:How should Vo and Theta should be chosen (and why), in order to making the distance X minimum? Consider that theta can be any number between 0 and 90 and Vo can go from 0 to a maximum value.
Express y as a function of x (hint: express t in terms of x and substitute into the expression for y as a function of t).
The minimum X distance will result when the projectile just misses the table. So there are two points: the take-off point and the end of the table. If v0 is not variable, then there is only one parabola that fits those two points. If v0 is variable, you want the parabola that has the greatest slope dy/dx as it passes the end of the table. That would be the parabola that has the greatest vertical speed at that point - ie the one that reaches the greatest height.
AM
mechanicsbook
- 3
- 0
X can be 0 if teta is90 and Vo is infinite so I consider the problem is not very well established,
cincirob
- 24
- 1
It seems to me the problem intends to ask what velocity produces the minimum x for a given angle between 0 and 90 degrees. It wil become clear why as the solution is given. The minimum x will occur for a given angle when the trajectory is such that the projectile just misses the corner of the step. The time it takes to traverse the hoizontal distance R is T(h) = R/(Vo*cos (theta)). The vertical component of velocity at that point in time will be the negative of the initial vertical velocity, so V=Vo + aT
-Vo=Vo + aT >> Vo= -aT/2. Substituing yields
Vo = -(-32.2ft/s/s)(R/(Vo*cos (theta))/2
Vo = (32.2*cos(theta)/2R)^.5
If I did the algebra correctly...be sure to check it, this will give Vo for a given theta. Since the cosine of 90 degrees is infinite, Vo could be infinite. That's the reason I chose to work it as a function of theta.
-Vo=Vo + aT >> Vo= -aT/2. Substituing yields
Vo = -(-32.2ft/s/s)(R/(Vo*cos (theta))/2
Vo = (32.2*cos(theta)/2R)^.5
If I did the algebra correctly...be sure to check it, this will give Vo for a given theta. Since the cosine of 90 degrees is infinite, Vo could be infinite. That's the reason I chose to work it as a function of theta.
Andrew Mason
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 7,794
- 502
Should be:cincirob said:It seems to me the problem intends to ask what velocity produces the minimum x for a given angle between 0 and 90 degrees. It wil become clear why as the solution is given. The minimum x will occur for a given angle when the trajectory is such that the projectile just misses the corner of the step. The time it takes to traverse the hoizontal distance R is T(h) = R/(Vo*cos (theta)). The vertical component of velocity at that point in time will be the negative of the initial vertical velocity, so V=Vo + aT
-Vo=Vo + aT >> Vo= -aT/2. Substituing yields
Vo = -(-32.2ft/s/s)(R/(Vo*cos (theta))/2
Vo = (32.2*cos(theta)/2R)^.5
v_0 = -aT/2 = -gR/2v_0cos(\theta)
v_0 = -\sqrt{gR/2cos\theta}
So for a given initial speed, x will be minimum when:
cos\theta = -gR/2v_0^2
AM
Similar threads
- Replies
- 32
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 8
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 8
- Views
- 813
- Replies
- 27
- Views
- 4K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 12
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 11
- Views
- 2K
Hot Threads
-
The problem of one tube and two balls on a plane
- Started by crazy lee
- Replies: 60
- Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Collision of a bullet on a rod-string system: query
- Started by palaphys
- Replies: 70
- Introductory Physics Homework Help
Recent Insights
-
Insights Quantum Entanglement is a Kinematic Fact, not a Dynamical Effect
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 7
- Quantum Physics
-
Insights What Exactly is Dirac’s Delta Function? - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 0
- General Math
-
Insights Relativator (Circular Slide-Rule): Simulated with Desmos - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 0
- Special and General Relativity
-
Insights Fixing Things Which Can Go Wrong With Complex Numbers
- Started by PAllen
- Replies: 7
- General Math
-
Insights Fermat's Last Theorem
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 91
- General Math
-
Insights Why Vector Spaces Explain The World: A Historical Perspective
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 0
- General Math