Boltzman Oscillation
- 233
- 26
- Homework Statement
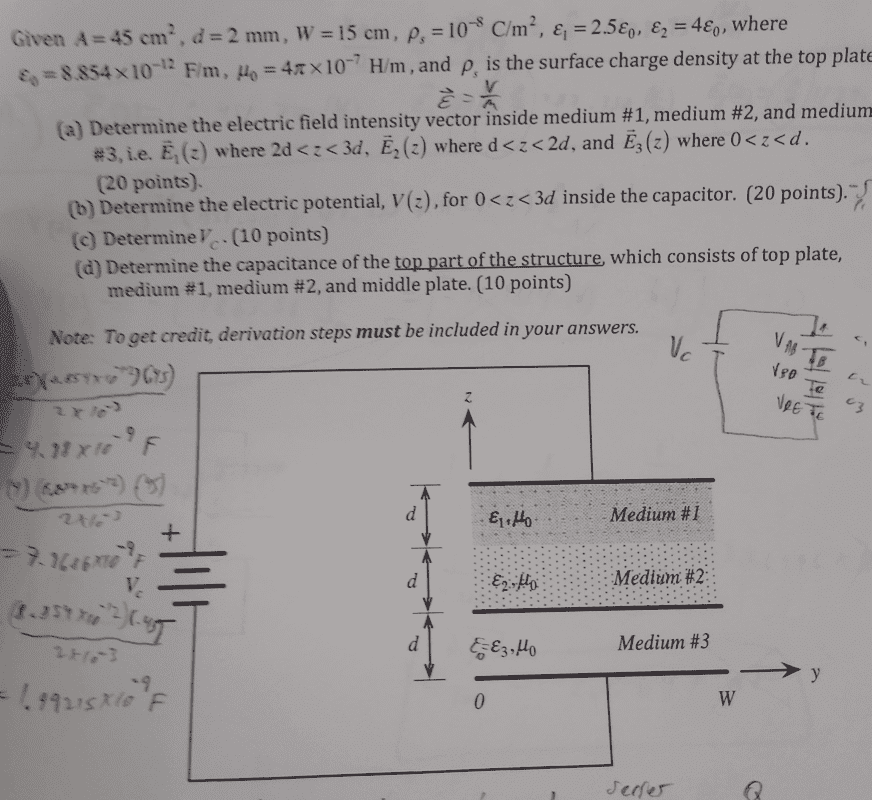
- The figure contains a capacitor consisting of three parallel conducting rectangular plates each of surface A, width W,. The plates are perfect dielectric conductors and non magnetic. The top and middle plates are separated by a distance 2d and filled with two dielectric layers. The middle and bottom plates are separated by a distance d and filled with air. The bottom plate i on the x-y plane. The voltage across the top and bottom plates is Vc. Determine the electric field intensity inside medium 1, 2, and 3. Determine the electric potential inside the capacitor.
- Relevant Equations
- Given below:
the image is given here along with some numerical information:
Now I know that the formula for the electric field in a capacitor is given as:
$$E = \frac{V}{d}$$
which I can use to obtain the three following fomulas:
$$E_1 = \frac{V_1}{d}$$
$$E_2 = \frac{V_2}{d}$$
$$E_3 = \frac{V_3}{d}$$
where I have used the fact that d is equal in all three mediums.
The total voltage is simply the addition of all of their voltages: V = V1 + V2 + V3.
Now I will attempt to find my boundary conditions.
Between medium 1 and medium 2 since they are both dielectric then the following is true:
$$\epsilon_1 E_{1n} - \epsilon_2 E_{2n} = p_s$$
Now I need the boundary conditions between medium 2 and medium 3.
Since there is a plate between medium 2 and 3 I will use the boundary conditions for a dielectric (medium 2) and conductor.
$$\epsilon_1 E_2 = \hat{n}p_s$$
I do not understand what to do now, am I working this out correctly or am I missing something. All help is appreciated.
Now I know that the formula for the electric field in a capacitor is given as:
$$E = \frac{V}{d}$$
which I can use to obtain the three following fomulas:
$$E_1 = \frac{V_1}{d}$$
$$E_2 = \frac{V_2}{d}$$
$$E_3 = \frac{V_3}{d}$$
where I have used the fact that d is equal in all three mediums.
The total voltage is simply the addition of all of their voltages: V = V1 + V2 + V3.
Now I will attempt to find my boundary conditions.
Between medium 1 and medium 2 since they are both dielectric then the following is true:
$$\epsilon_1 E_{1n} - \epsilon_2 E_{2n} = p_s$$
Now I need the boundary conditions between medium 2 and medium 3.
Since there is a plate between medium 2 and 3 I will use the boundary conditions for a dielectric (medium 2) and conductor.
$$\epsilon_1 E_2 = \hat{n}p_s$$
I do not understand what to do now, am I working this out correctly or am I missing something. All help is appreciated.