kissafilipino
- 7
- 0
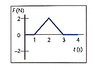
1. I understand I need to find the area underneath the force time graph, however I do not understand how to use the impulse = m(delta)v
2. the question says:
A 0.145 kg ball, moving in the positive direction at 13 m/s, is acted on by the impulse shown in the graph in Figure 9-12 What is the ball's speed at 4.0 s?
Here is the image: http://www.webassign.net/glencoe99/9-12.gif
3. all the info is relevant, however it confuses me because I don't understand the underthegraph thing that is suppose to help me solve
2. the question says:
A 0.145 kg ball, moving in the positive direction at 13 m/s, is acted on by the impulse shown in the graph in Figure 9-12 What is the ball's speed at 4.0 s?
Here is the image: http://www.webassign.net/glencoe99/9-12.gif
3. all the info is relevant, however it confuses me because I don't understand the underthegraph thing that is suppose to help me solve