edwin.07
- 4
- 0
1. Given the set-up in Figure 1, how much work will be done after part of the weight is removed, as shown in Figure 2, knowing only the height the piston rises?
2. W=mC[P](T[2]-T[1])+mg(h[2]-h[1])
3. W=mC[P](T[2]-T[1])+(m[2]-m[1])g(h[2]-h[1])
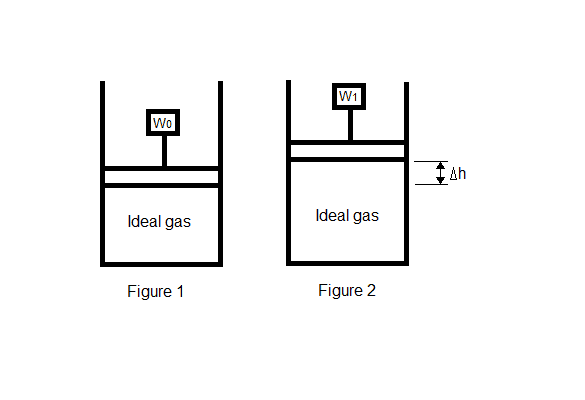
2. W=mC[P](T[2]-T[1])+mg(h[2]-h[1])
3. W=mC[P](T[2]-T[1])+(m[2]-m[1])g(h[2]-h[1])
Last edited: