- #1
medo
- 4
- 0
Hello all,
Thank you for reading my topic. My client asked me to make calculation sheet for gas pipeline like the image below. Can someone help me to make this? (i'm new in this system, need to learn and study. So please help me)
How to calculate the required pressure at connection point if knowing pressure outlet, pipe diameter, length of gas (N2 – Nitrogen) pipe like image below? (Neglect pressure loss through fittings, valve and deferent high level of connection point and end point)
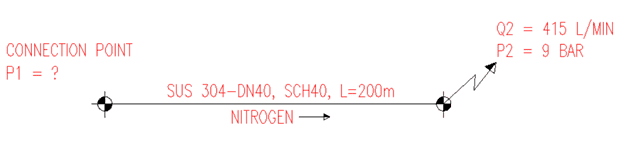
Thanks in advance
Thank you for reading my topic. My client asked me to make calculation sheet for gas pipeline like the image below. Can someone help me to make this? (i'm new in this system, need to learn and study. So please help me)
How to calculate the required pressure at connection point if knowing pressure outlet, pipe diameter, length of gas (N2 – Nitrogen) pipe like image below? (Neglect pressure loss through fittings, valve and deferent high level of connection point and end point)
Thanks in advance