- #1
CCenturion
- 3
- 0
Homework Statement
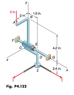
The assembly shown is used to control the tension T in a tape that passes around a frictionless spool at E. Collar C is welded to rods ABC and CDE. It can rotate about shaft FG but its motion along the shaft is prevented by a washer S. For the loading shown, determine (a) the tension T in the tape, (b) the reaction at C.
Homework Equations
In the solution manual it says the reactions are as follows, C = <Cx,Cy,Cz> and M=<0,My,Mz>
Actually, C i kind of understand it, but not tally sure, and M i have no clue…
The Attempt at a Solution
I Just need help regarding the direction of the forces and couples.
My understanding is that because there's a welded connection, the weld will provide support from moving the rods, therefore the reaction at C goes in the x,y and z directions. However, if there's a vertical downforce at the end of the rod ( 6 lb) wouldn't that cause a rotation about FG and therefore cause a couple in the z direction only?